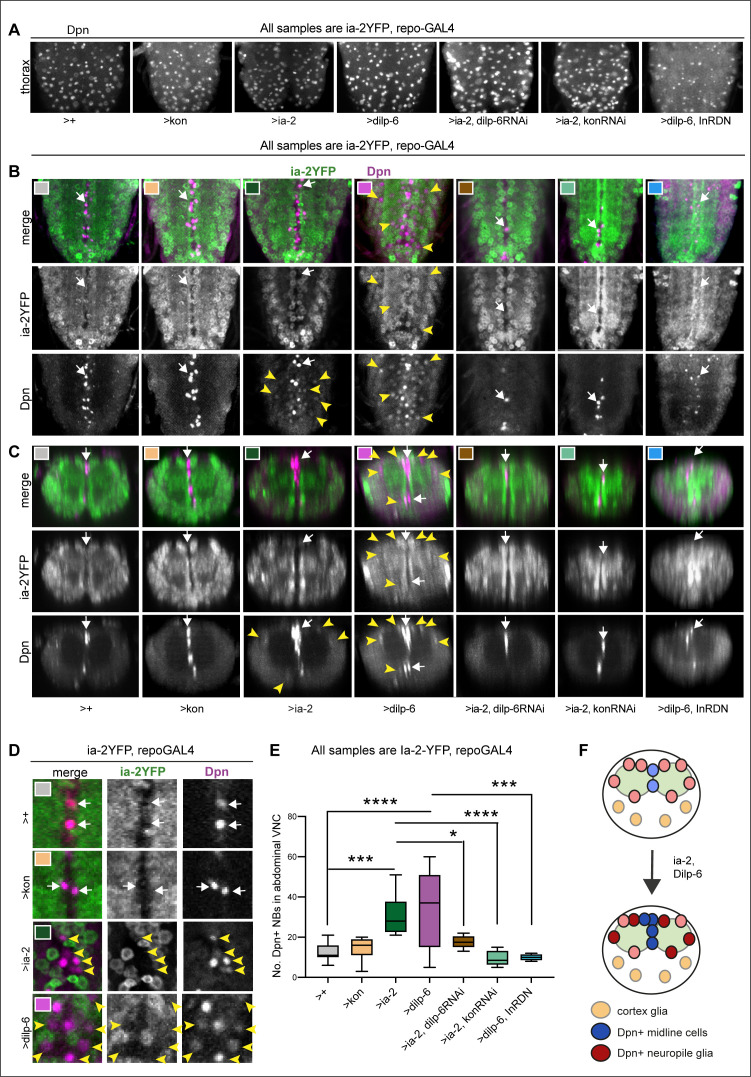
Figure 6. Ia-2 and Dilp-6 induce ectopic neural stem cells from InR signalling in glia.
All samples were analysed at 120 hr AEL, after disappearance of abdominal developmental neuroblasts. (A) Dpn signal in thorax was normally strong and clear, except with the overexpression of both dilp-6 and InRDN in glia, which reduced Dpn levels and NB size. (B and C) Overexpression of ia-2 and dilp-6, but not kon-full-length, induced Dpn+ cells in the abdominal ventral nerve cord (VNC), at the midline and in lateral positions. Ectopic abdominal Dpn was at lower levels than normal thoracic signal in NBs. (D) Ectopic Dpn+ cells did not express Ia-2YFP (arrowheads). (E) Overexpression of ia-2 or dilp-6 increased abdominal Dpn+ cell number. Quantification of all abdominal VNC Dpn+ cells, and genetic epistasis analysis showing that: the increase in Dpn+ cell number caused by ia-2 overexpression was rescued by dilp-6 RNAi and kon-RNAi knock-down in glia, meaning that ia-2 requires Dilp-6 and glial Kon to induce Dpn; and preventing insulin signalling with InRDN in glia rescued the increase in Dpn+ cell number caused by dilp-6 overexpression, meaning that Dilp-6 induced Dpn via InR signalling in glia. One-way ANOVA p<0.0001, post hoc Tukey’s test multiple comparisons all samples vs. all. N = 5–13 VNCs. (F) Illustration showing that Ia-2 and Dilp-6 can induce Dpn via InR signalling in glial cells. (A and B) Horizontal views; (C) transverse views; (D) higher magnification. Graphs show quantifications in box-plots. Asterisks refer to multiple comparison post hoc tests: *p<0.05, ***p<0.0001, ****p<0.0001. For full genotypes and further statistical analysis details, see Supplementary file 1.
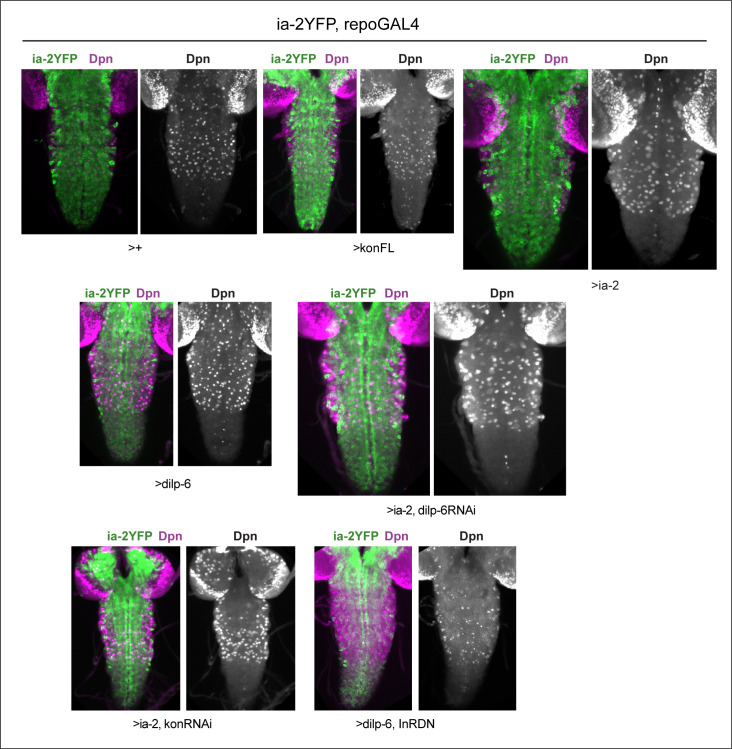
Figure 6—figure supplement 1. Dpn in thoracic neuroblasts of specimens shown in Figure 6.
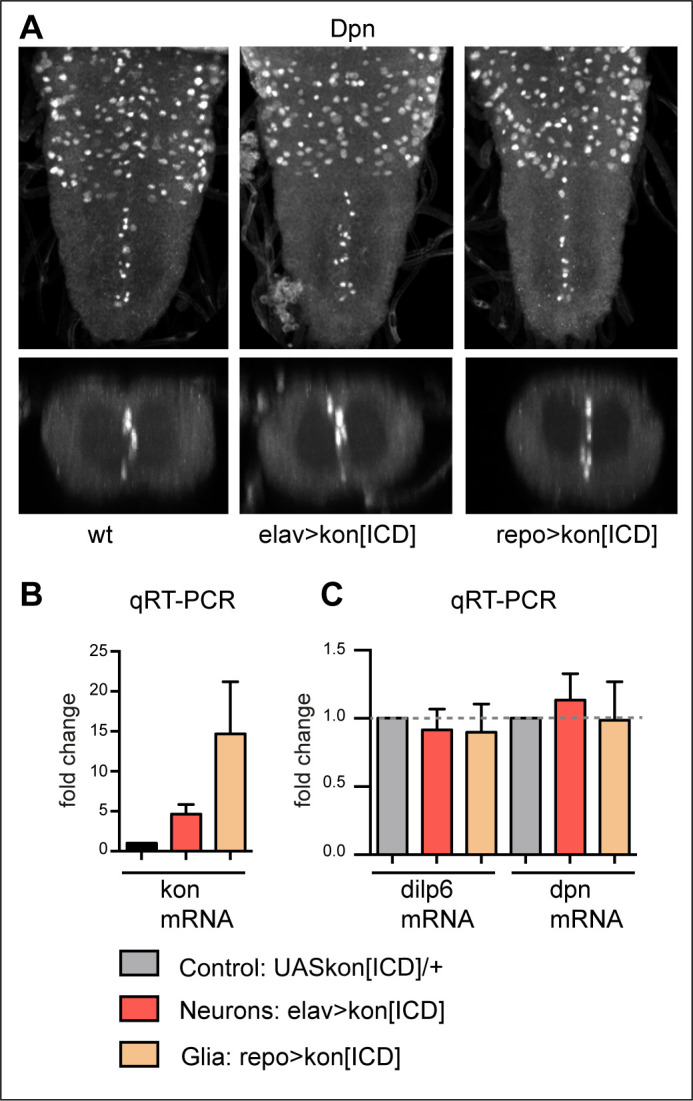
Figure 6—figure supplement 2. KonICD does not induce dilp-6 nor dpn expression.