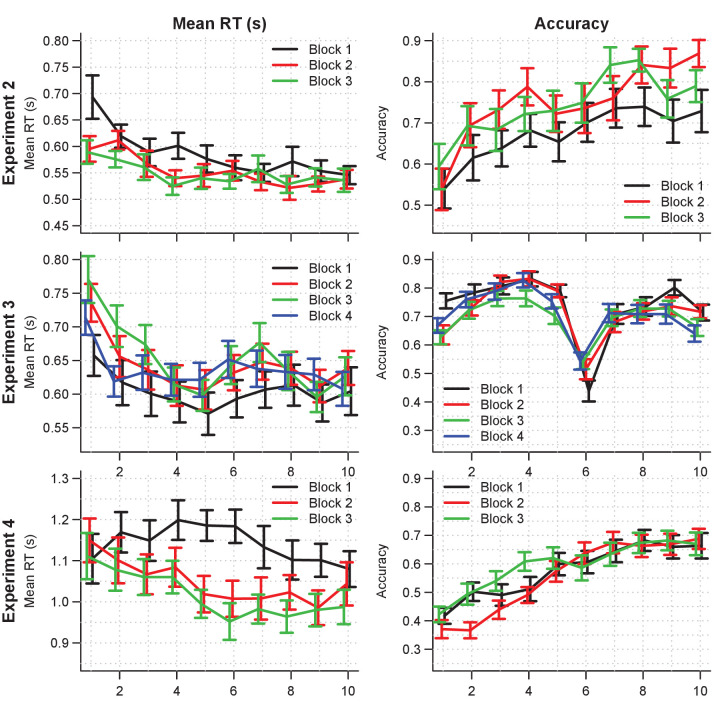
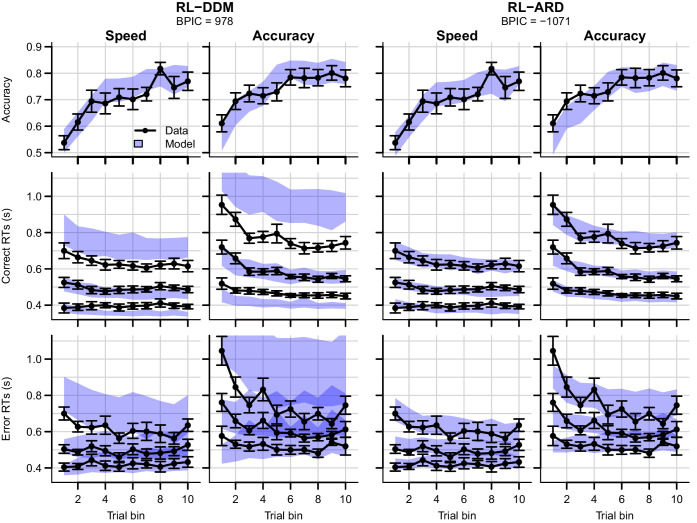
Block numbers are color-coded. Error bars are 1 SE. Mixed effects models indicated that in experiment 2, RTs decreased with block number (b = −0.04, SE = 6.15*10−3, 95% CI [−0.05,–0.03], p = 6.61*10−10) as well as with trial bin (b = −0.02, SE = 2.11*10−3, 95% CI [−0.02,–0.01], p = 1.68*10−13), and there was an interaction between trial bin and block number (b = 3.61*10−3, SE = 9.86*10−4, 95% CI [0.00, 0.01], p = 2.52*10−4). There was a main effect of (log-transformed) trial bin on accuracy (on a logit scale; b = 0.36, SE = 0.11, 95% CI [0.15, 0.57], p = 7.99*10−4), but no effect of block number, nor an interaction between block number and trial bin on accuracy. In experiment 3, response times increased with block number (b = 0.02, SE = 3.10*10−3, 95% CI [0.01, 0.02], p = 1.21*10−7), decreased with trial bin (b = −4.24*10−3, SE = 1.37*10−3, 95% CI [−6.92*10−3, −1.56*10−3], p = 0.002), but there was no interaction between trial bin and block number (b = −9.15*10−4, SE = 5*10−4, 95% CI [0.00, 0.00], p = 0.067). The bottom left panel suggests that the main effect of block number on RT is largely caused by an increase in RT after the first block. Accuracy decreased with (log-transformed) trial bin (on a logit scale: b = −0.12, SE = 0.05, 95% CI [−0.22,–0.02], p = 0.02), decreased with block number (b = −0.08, SE = 0.03, 95% CI [−0.14,–0.02], p = 0.009), but there was no interaction (b = 0.02, SE = 0.02, 95% CI [−0.02, 0.06], p = 0.276). The decrease in accuracy with trial bin is expected due to the presence of reversals. The combination of an increase in RT and a decrease in accuracy after the first block could indicate that participants learnt the structure of the task (i.e. the presence of reversals) in the first block, and adjusted their behavior accordingly. In line with this speculation, the accuracy in trial bin 6 (in which the reversal occurred) was lowest in the first block, which suggests that participants adjusted to the reversal faster in the later blocks. In experiment 4, response times decreased with block number (b = −0.04, SE = 9.08*10−3, 95% CI [−0.06,–0.02], p = 3.19*10−3) and there was an interaction between block number and trial bin (b = −4.31*10−3, SE = 1.45*10−3, 95% CI = [−0.01, 0.00], p = 0.003), indicating that the decrease of RTs over trial bins was larger for the later blocks. There was no main effect of trial bin on RTs. There was a main effect of (log-transformed) trial bin on accuracy (on a logit scale: b = 0.60, SE = 0.07, 95% CI [0.47, 0.73], p < 10-16), but no main effect of block and no interaction between block and trial bin.