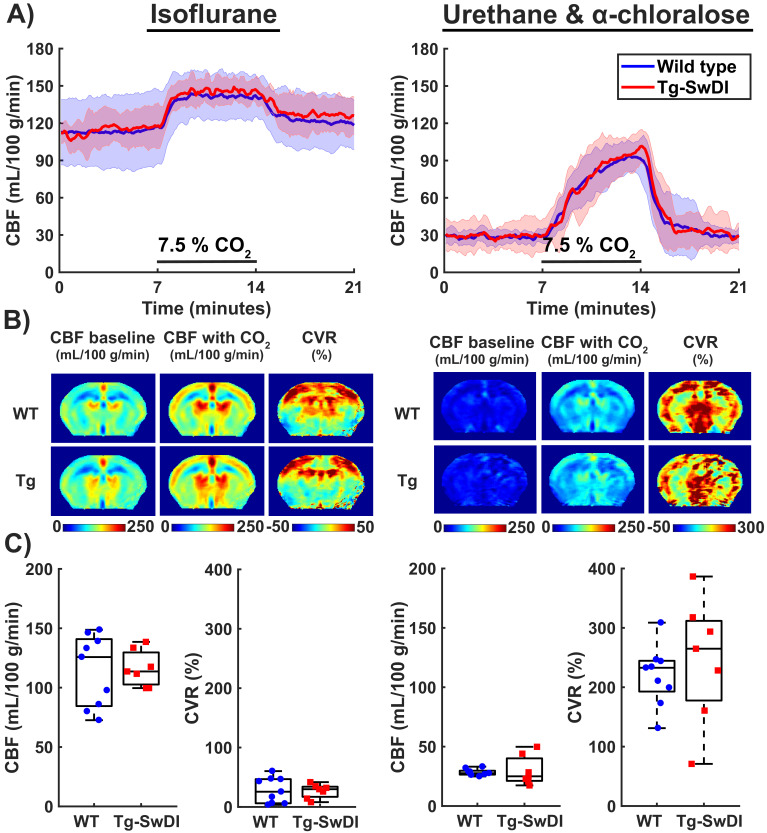
Figure 5. Cerebral blood flow (CBF) and cerebrovascular reactivity (CVR) acquired during isoflurane anesthesia and urethane and α-chloralose (U and A) anesthesia.
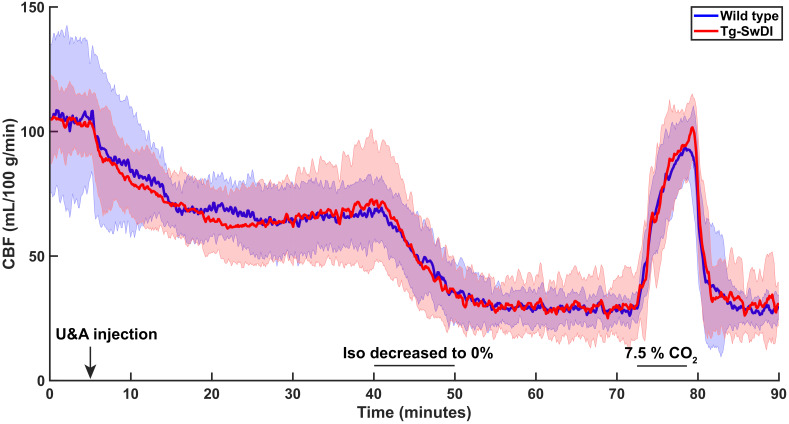
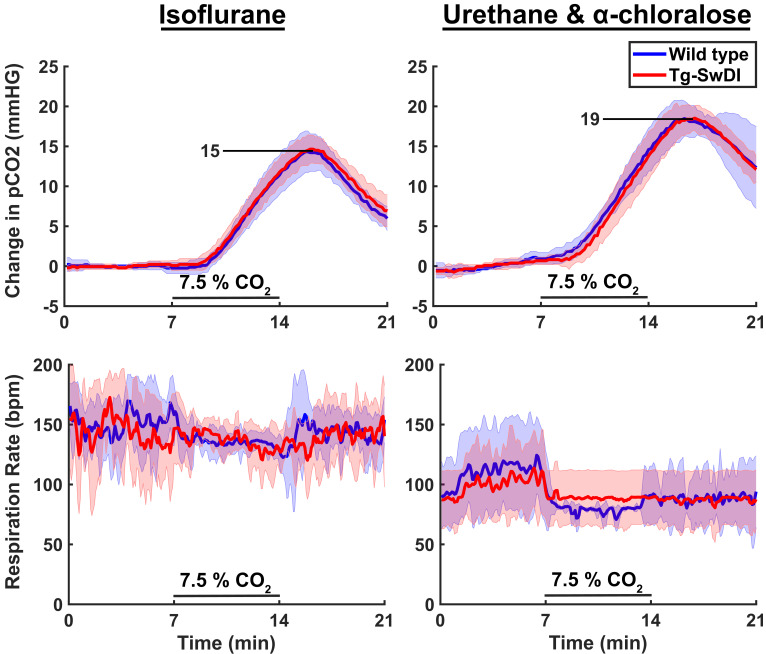
(A) 21-min CBF time profiles acquired in the mid-brain in wild-type (WT) and transgenic Swedish Dutch Iowa (Tg-SwDI) mice under either isoflurane anesthesia (left, 12 months old) or U and A anesthesia (right, 10 days later in the same mice). CO2 was administered between minutes 7 and 14. (B) Mid-brain CBF and CVR maps averaged for WT (top) and Tg-SwDI (bottom) mice. Note that the CVR maps during U and A anesthesia are scaled differently than the CVR maps under isoflurane due to the marked difference in CVR. (C) Boxplot representations of the baseline CBF and CVR group values, where dots and circles represent individual mice.