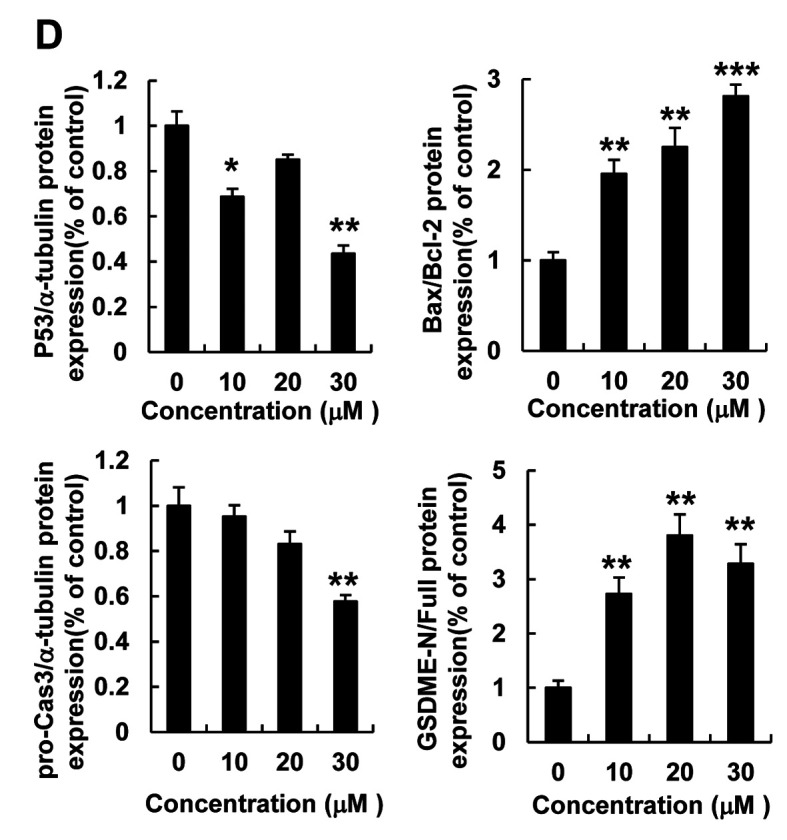
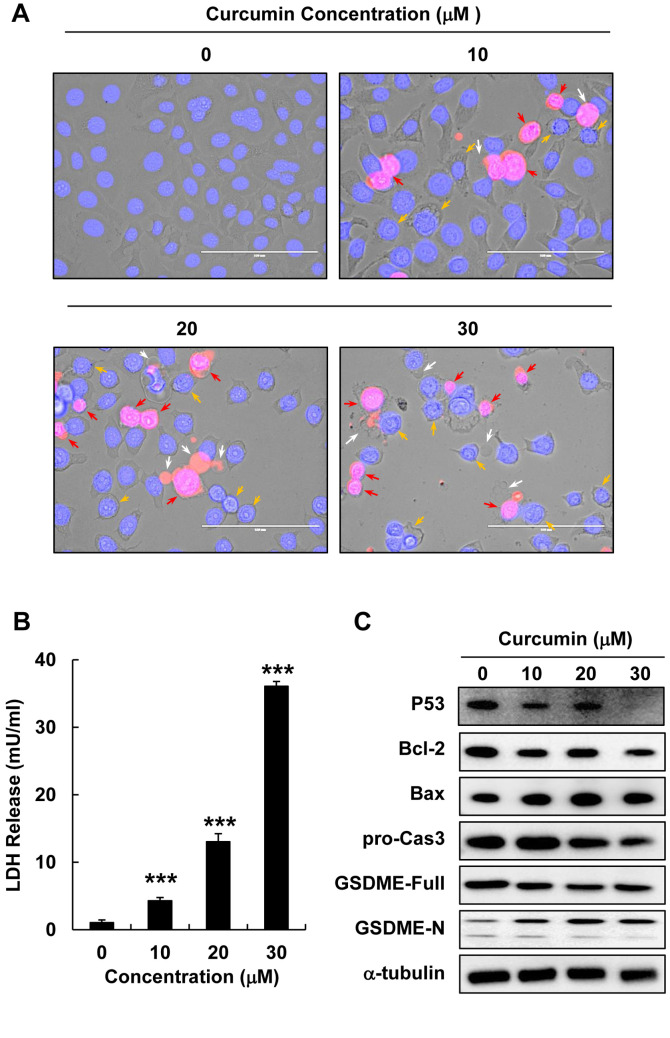
Figure 2. Curcumin induced lytic cell death and pyroptosis in HepG2 cells. HepG2 cells were treated with curcumin (0, 10, 20, or 30 μM) for 12 h. (A) Morphological changes and pyroptosis were observed using fluorescence microscopy in PI (red)- and Hoechst (blue)-stained HepG2 cells treated with curcumin (0, 10, 20, or 30 μM) (scale bar=100 μm). (B) LDH release in HepG2 cells treated with curcumin (0, 10, 20, or 30 μM). (C) Bcl-2, Bax, pro-caspase3, GSDME-Full, and GSDME-N protein expression detected using western blot analysis in HepG2 cells treated with curcumin (0, 10, 20, or 30 μM). (D) Quantitative analysis of Bcl-2, pro-caspase3, and GSDME-N protein expression presented as the mean±SEM of three different samples (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001).