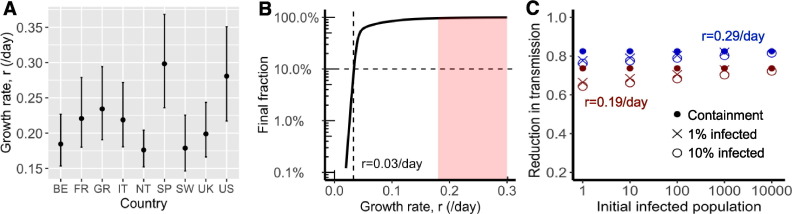
Fig. 2.
Fast spread of SARS-CoV-2 and its implications for public health interventions. (A) Point estimates and confidence interval ranges of the exponential growth rate, in each country. See Table 2 for country name abbreviations. (B) Final fraction of infected individuals after 12 months of outbreak. A growth rate less than 0.03/day, i.e. a doubling time of 23 days, is needed to achieve the goal that less than 10% of individuals are infected (dashed lines). However, the benefit, i.e. fraction of uninfected individuals, increases exponentially when the growth rate is further reduced beyond the threshold. (C) High levels of control efforts, measured as fractions of transmission reduction (y-axis), are needed to achieve containment, i.e. reverting epidemic growth (dots), or mitigation, i.e. the final fraction of infected individuals is 1% (x) or 10% (open circle) after a year. We assumed initial infected population as shown in x-axis and epidemic growth rates of 0.19 (red) or 0.29/day (blue).