Extended Data Fig. 8. ATPase activity, H4 interaction and macrodomains of ALC1 are essential for protecting BRCA-mutant cells from ola hypersensitivity.
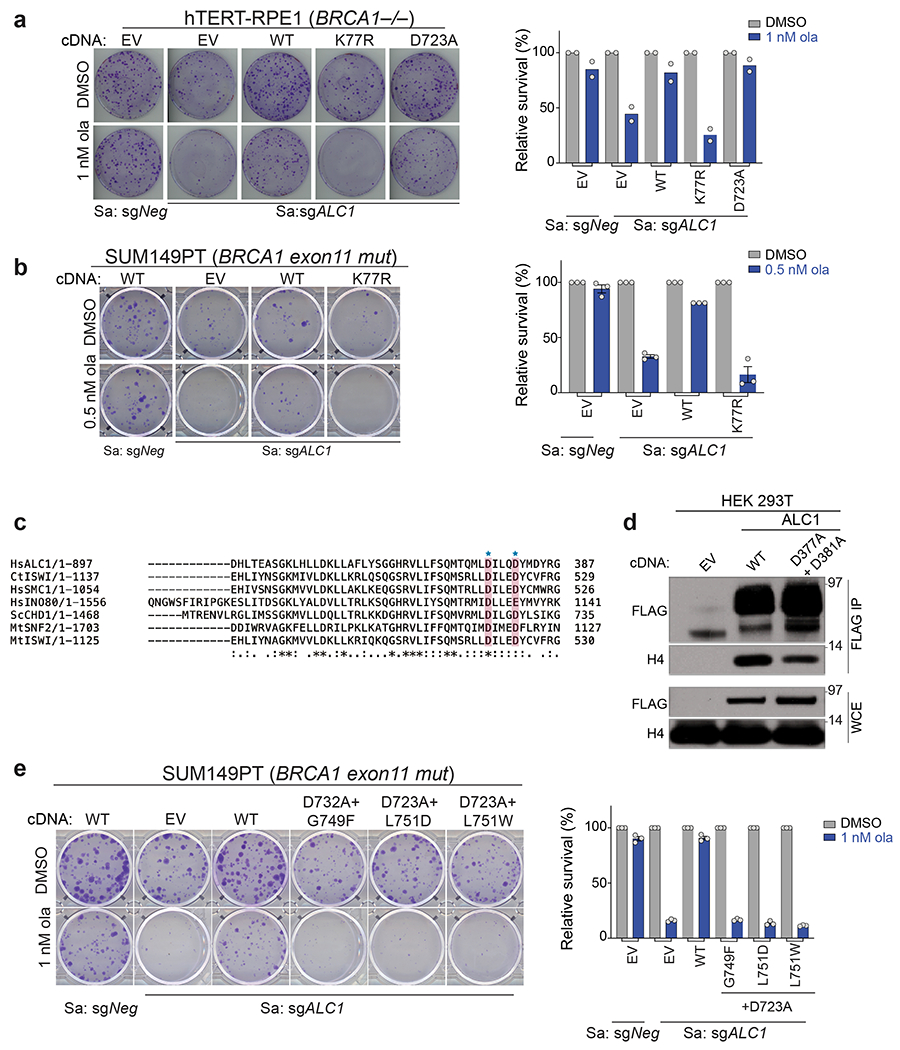
a, Representative images (left) and quantification (right) of the clonogenic survival assay using hTERT-RPE1 BRCA1−/− cells expressing sgALC1 and the indicated ALC1 mutants treated with ola (1 nM). Data are mean from two biologically independent experiments. b, Representative images (left) and quantification (right) of the clonogenic survival assay (left) using SUM149PT cells expressing sgALC1 and ALC1 K77R mutant treated with ola (0.5 nM). Data are mean ± s.e.m from n = three independent experiments. Number of colonies in the ola treated condition were normalized to its respective untreated counterpart. c, Sequence alignment of various chromatin remodelers using Clustal Omega. Histone H4 interacting residues as predicted by PDB:6PWF are highlighted and marked by a blue star. d, Immunoblots showing interactions of FLAG ALC1 WT and FLAG ALC1 D377A+ D381A with histone H4. Experiment was repeated twice with similar outcomes. e, Representative images of the clonogenic survival assay (left) and quantification (right) of SUM149PT cells expressing sgALC1 and indicated ALC1 macrodomain mutants treated with ola (1 nM). Data are mean ± s.e.m. from n = three independent experiments. Number of colonies in the ola treated condition were normalized to its respective untreated counterpart. Source data are provided.
