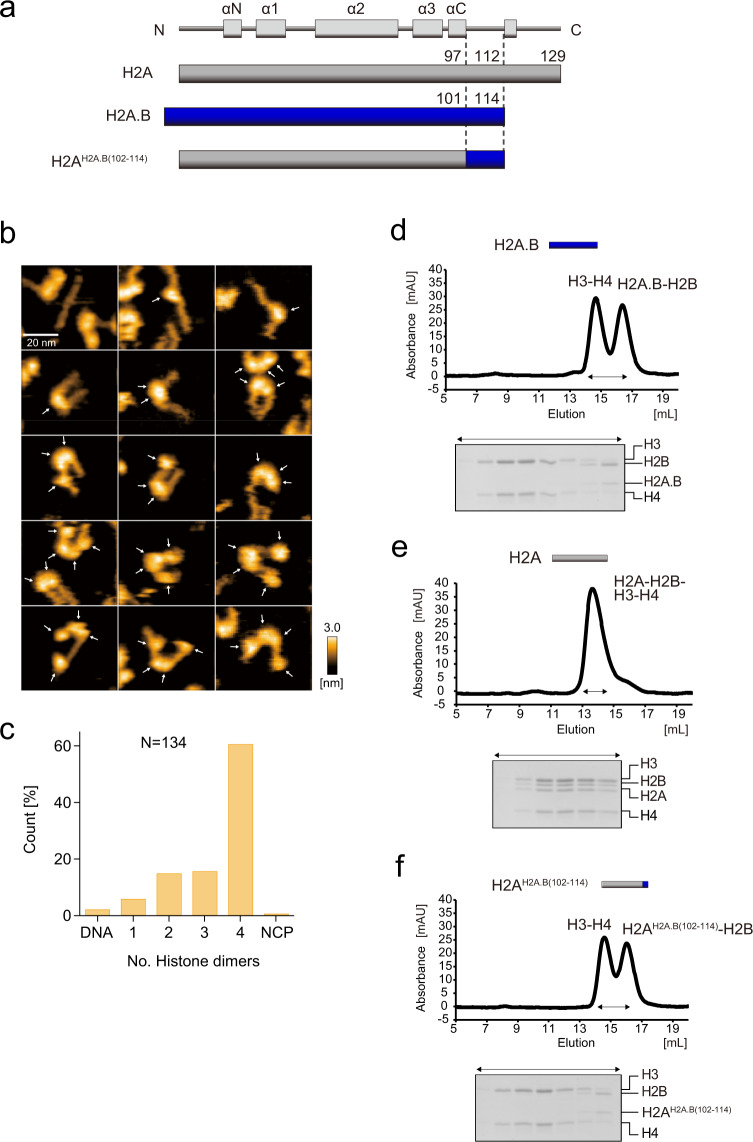
Fig. 5. HS-AFM observation and histone octamer formation assay of the H2AH2A.B(102–114) NCP.
a Graphical representation of the chimeric protein used in the HS-AFM observations shown in (b, c) and the histone octamer formation assay shown in (d–f). b Initial HS-AFM images of the H2AH2A.B(102–114) NCP. Individual particles are presented in the panels. White arrows indicate possible histone dimers. Scale bars are 20 nm. c The numbers of histone dimers in individual particles were counted and plotted. N indicates the total number of the counted particles. The source data for HS-AFM analysis are shown in Supplementary Data 1. d–f The H3-H4 tetramers were mixed with the H2A.B-H2B dimer (d), the H2A-H2B dimer (e), or the H2AH2A.B(102–114)-H2B dimer (f), and incubated in the presence of 2 M NaCl at 37 °C for 30 min. After the incubation, the samples were subjected to chromatography on a Superdex 200 10/300 GL column. Histone compositions of the peak fractions were analyzed by 18% SDS-PAGE with CBB staining. Reproducibility is confirmed by two independent experiments, and the results are presented in Supplementary Fig. 7. The uncropped gel images are shown in Supplementary Fig. 9.