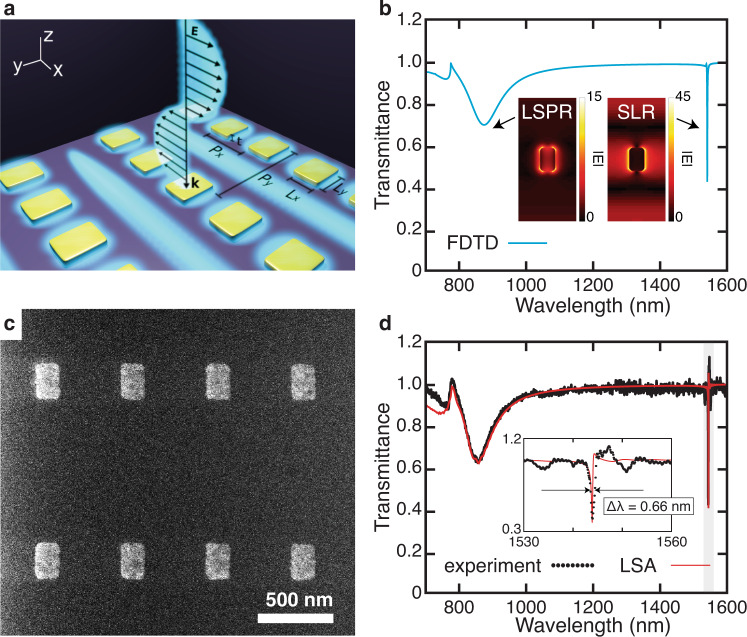
Fig. 1. High-Q metasurface nanocavities using arrays of plasmonic nanostructures.
a Schematic of the metasurface consisting of a rectangular array of rectangular gold nanostructures. Here Lx = 130 nm, Ly = 200 nm, t = 20 nm, Px = 500 nm, and Py = 1060 nm. The blue shaded regions illustrate the electric field, reproducing the mode structure in the inset of b. b Numerical (FDTD) calculations of the transmission spectrum of this metasurface for x-polarized light. Both the LSPR and the SLR are observed in these results. Inset: The simulated magnitude of the electric field ∣E∣ for the entire unit cell of both LSPR and SLR modes in the x–y plane that bisects the nanoparticles. The color bar indicates the relative magnitude when normalized to the incident plane wave. c Helium ion microscopic image of the fabricated metasurface prior to cladding deposition. d Measured transmission spectrum (black dots) and fits to semi-analytic calculations (LSA, red line). Inset: Zoomed plot of the highlighted region in d. Fitting the measurement to a Lorentzian function yields a linewidth of Δλ = 0.66 nm, corresponding to Q = 2340 (see Supplementary Sec. S1: Q-factor extraction).