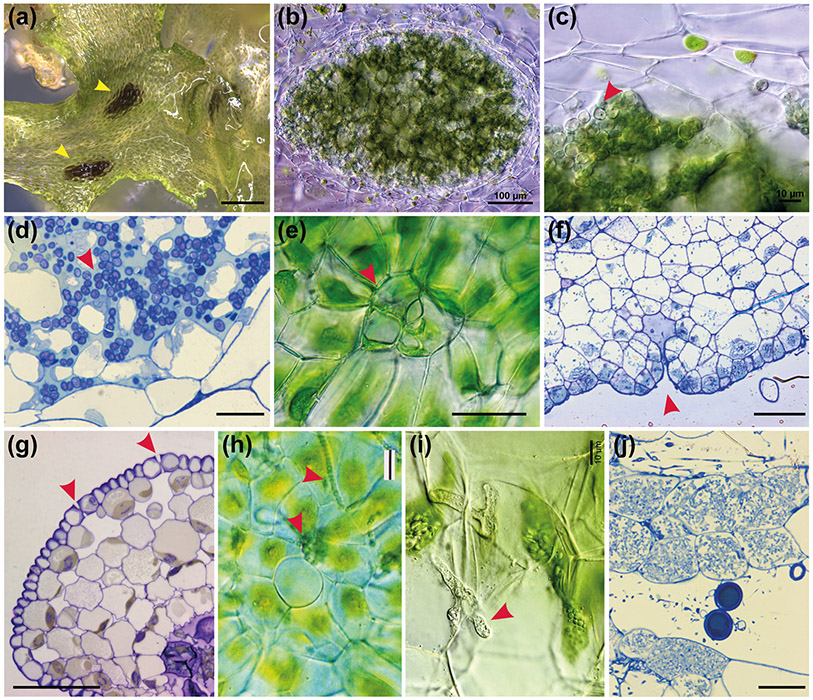
Fig. 8: Hornwort symbiotic relationships.
(a) Surface view of A. puncatus thallus colonised by cyanobacteria (yellow arrowheads). Scale bar: 450 μm. (b-c) Hand sections of A. punctatus thallus showing ellipsoidal cavities colonised by cyanobacteria. In (c) cyanobacteria indicated with red arrowhead Scale bars: 100 μm (b) and 10 μm (c). (d) LM section of Nostoc colony showing algal cells (red arrowhead) with intermingling gametophyte cells in A. agrestis. Scale bar: 10 μm (e) LM surface view of ventral mucilage cleft. Scale bar: 15 μm. (f) Longitudinal section of a mucilage cleft (red arrowhead) leading to small intercellular space near apical notch of A. agrestis. Scale bar: 50 μm (g) LM transverse section of sporophyte showing guard cell in epidermis that lead to substomatal cavities. Guard cells are larger than epidermal cells and have differentially thickened cell walls with inner and outer ledges and are different from mucilage cleft cells in (f) that have evenly thickened walls. Scale bar: 50 μm. (h) LM showing surface view of a mucilage cleft and attracted cyanobacteria just entered the cleft in Phaeoceros carolinianus. Scale bar:20 μm (i, j) Hornwort symbiotic relationship with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Hand section LM of P. carolinianus thallus cells with fungal hyphae (red arrowhead). Scale bar: 10 μm. (j) LM section of gametophyte cells containing vesicles (circles) and arbuscules (masses of hyphae in cells). Scale bar: 20 μm