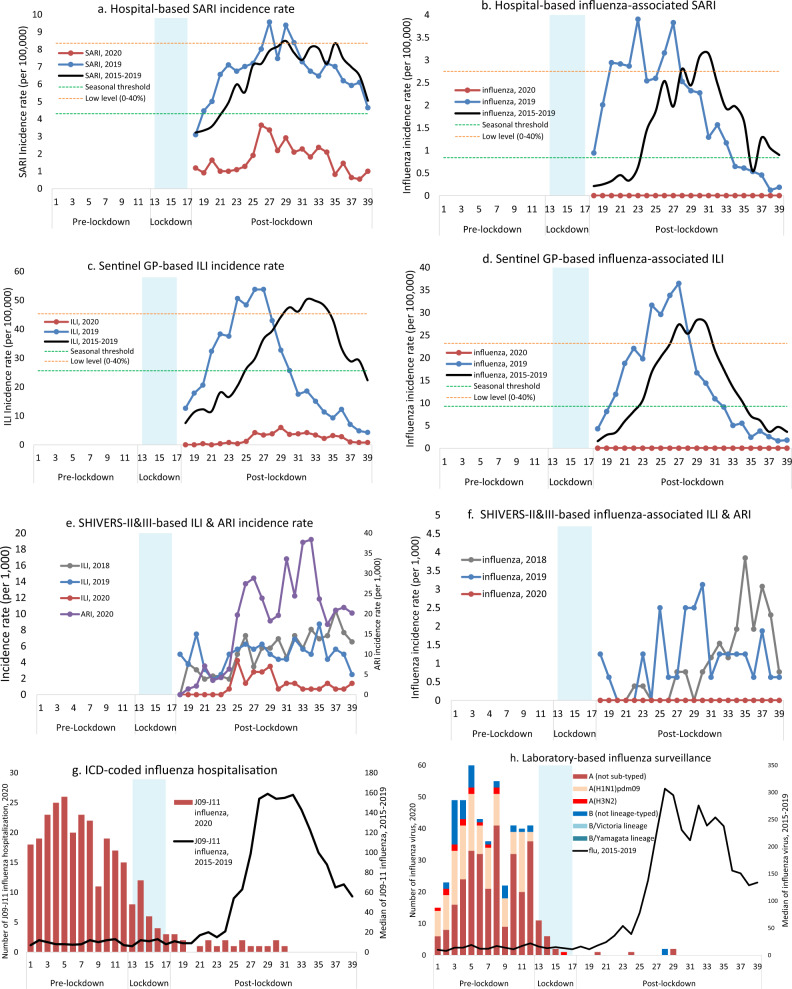
Fig. 1. Temporal distribution of acute respiratory illness and associated influenza infections in 2020 compared with previous years.
a, b Hospital-based SARI incidence rate and influenza-associated SARI. c, d Sentinel GP-based ILI incidence rate and influenza-associated ILI. e, f SHIVERS-II&III-based ILI and ARI incidence rate and influenza-associated ILI and ARI. g ICD-coded influenza hospitalisation. h Laboratory-based influenza surveillance. SARI severe acute respiratory illness, GP general practice, ILI influenza-like illness, ARI acute respiratory illness, SHIVERS-II&III the second and third iterations of the Southern Hemisphere Influenza and Vaccine Effectiveness Research and Surveillance programme, ICD International Classification of Diseases, flu refers to influenza. The calculation for epidemic threshold and low influenza activity is described in “Methods”. A patient with cough and history of fever (subjective fever or measured temperature ≥38 °C) and onset within the past 10 days meets the SARI case definition if hospitalised or meets the ILI case definition if consulting a GP or participating in the SHIVERS-II&III study. The ARI case definition among SHIVERS-II&III participants refers to an acute respiratory illness with fever or feverishness and/or one of the following symptoms (cough, running nose, wheezing, sore throat, shortness of breath, loss of sense of smell/taste) with onset in the past 10 days.