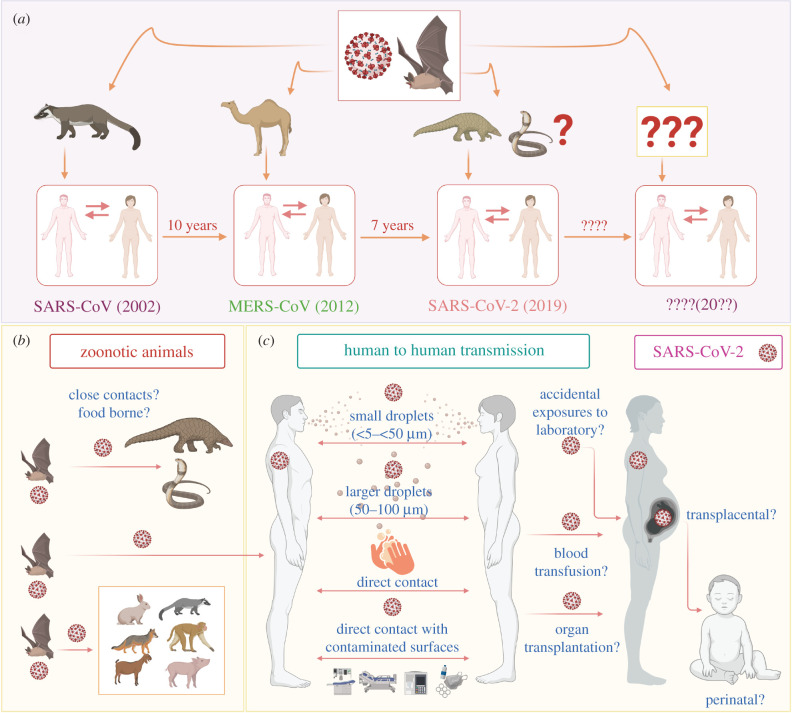
Figure 1.
Origin of coronavirus and potential routes of transmission of SARS-CoV-2. (a) The origin of coronavirus. Similar to SARS and MERS, coronavirus is an emerging virus that has crossed the species barrier from wild animals to humans. The origin of SARS-CoV-2 is also suspected to be from an intermediate animal host, and the likelihood of crossing the species barrier for a fourth time cannot be ruled out. The current COVID-19 outbreak caused by SARS-CoV-2 has already been predicted and will also be contained sooner or later, similar to earlier outbreaks [15]. However, the real issue is how we plan to counter the next zoonotic CoV pandemic that is likely to occur in the next 5 to 10 years, if not sooner. (b,c) The potential routes of transmission of SARS-CoV-2. SARS-CoV-2 is alleged to have zoonotic (animal-to-human) origin with further human-to-human transmission [16], and the likelihood of food-borne transmission should be ruled out pending further investigation [17]. In addition, it can potentially be transmitted through direct contact, as in other respiratory viruses, such as by shaking contaminated hands or exposure to contaminated surfaces (fomite transmission). Nevertheless, other possible routes of SARS-CoV-2 transmission, such as accidental exposure to the laboratory, blood transfusion, organ transplantation [18], and transplacental and perinatal routes, need to be adduced more concretely. SARS-CoV: severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus, MERS-CoV: Middle East respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2: severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.