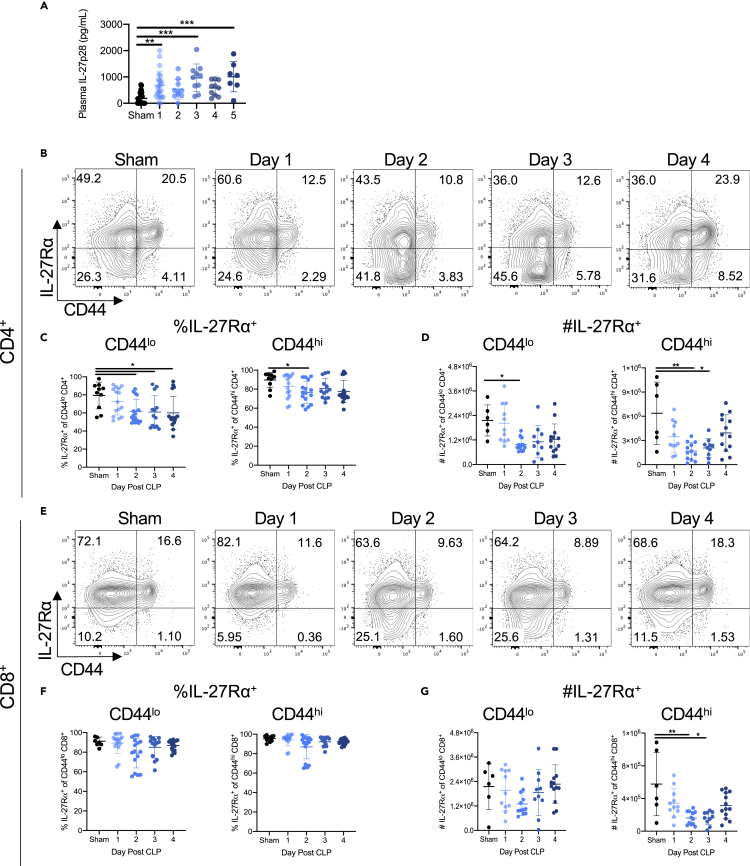
Figure 1.
Sepsis results in a reduction in the frequency and number of IL-27Rα+ T cells
Following cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) or sham surgery (sham), animals were euthanized on the indicated days. Plasma was collected for IL-27p28 ELISAs on days 1 through 5 and spleens harvested for analysis by flow cytometry on days 1 through 4.
(A) Concentration of IL-27p28 in the plasma of sham and CLP mice on days 1 through 5 following surgery.
(B) Representative flow cytometric plots showing the frequency of IL-27Rα expressing CD4+ T cells in sham and CLP mice on days 1–4 after surgery.
(C) The frequency of CD4+ CD44lo naive (left) and CD4+ CD44hi memory (right) T cells expressing the IL-27Rα in sham and CLP mice on days 1–4 after surgery.
(D) The absolute number of CD4+ CD44lo naive (left) and CD4+ CD44hi memory (right) T cells expressing the IL-27Rα in sham and CLP mice on days 1–4 after surgery.
(E) Representative flow cytometric plots showing the frequency of IL-27Rα expressing CD8+ T cells in sham and CLP mice on days 1–4 after surgery.
(F) The frequency of CD8+ CD44lo naive (left) and CD8+ CD44hi memory (right) T cells expressing the IL-27Rα in sham and CLP mice on days 1–4 after surgery.
(G) The absolute number of CD8+ CD44lo naive (left) and CD8+ CD44hi memory (right) T cells expressing the IL-27Rα in sham and CLP mice on days 1–4 after surgery. All summary data were pooled from three independent experiments, with n = 7–18 mice per group. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Error bars represent the mean ± the standard deviation.