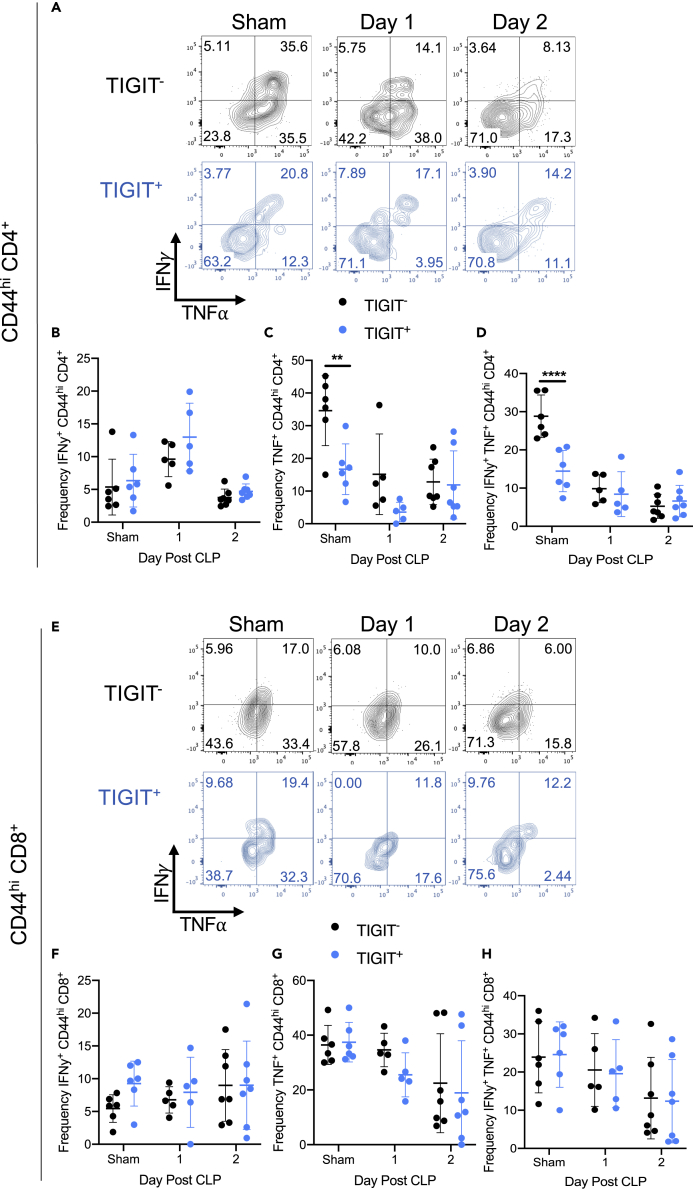
Figure 8.
TIGIT is not associated with the impairments observed in cytokine production
CLP and sham surgery (“sham”) were performed on wild-type mice. One and two days after surgery, splenocytes were harvested for stimulation with PMA/Ionomycin or incubated without stimulation. Following incubation, samples were stained for TIGIT, IFN-γ, and TNF-α and assessed by flow cytometry.
(A) Representative flow cytometric plots of IFN-γ (y axis) and TNF-α (x axis) production by TIGIT− (black) and TIGIT+ (blue) CD44hi memory CD4+ T cells following surgery.
(B) The frequency of IFN-γ producing TIGIT− (black) and TIGIT+ (blue) CD44hi memory CD4+ T cells following surgery.
(C) The frequency of TNF-α producing TIGIT− (black) and TIGIT+ (blue) CD44hi memory CD4+ T cells following surgery.
(D) The frequency of IFN-γ and TNF-α co-producing TIGIT− (black) and TIGIT+ (blue) CD44hi memory CD4+ T cells following surgery.
(E) Representative flow cytometric plots of IFN-γ (y axis) and TNF-α (x axis) production by TIGIT− (black) and TIGIT+ (blue) CD44hi memory CD8+ T cells of wild-type mice following sham or CLP surgery.
(F) The frequency of IFN-γ-producing TIGIT− (black) and TIGIT+ (blue) CD44hi memory CD8+ T cells following surgery.
(G) The frequency of TNF-α-producing TIGIT− (black) and TIGIT+ (blue) CD44hi memory CD8+ T cells following surgery.
(H) The frequency of IFN-γ and TNF-α co-producing TIGIT− (black) and TIGIT+ (blue) CD44hi memory CD8+ T cells following surgery. Data are representative of two experiments with n = 5–7 mice per group. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. Error bars represent the mean ± the standard deviation.