Figure 1.
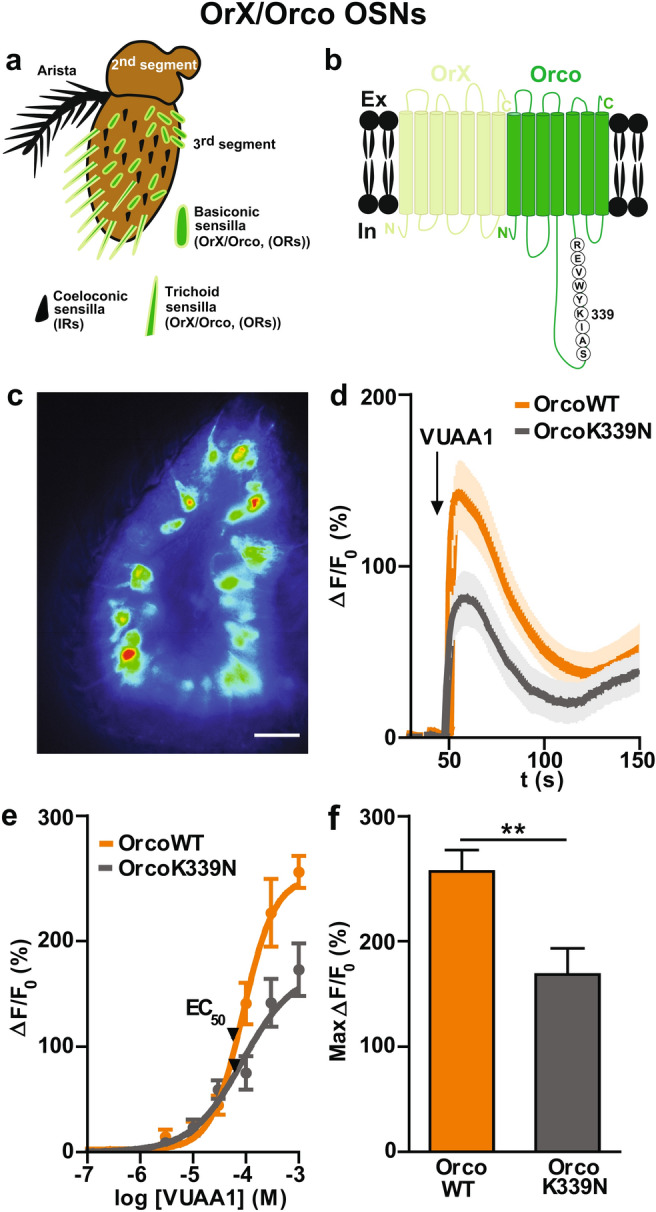
Effect of Orco CBS mutation on the odor response in OrX/Orco expressing OSNs. (a) Scheme of a Drosophila melanogaster antenna. The third segment is covered with sensilla that house the dendrites of up to four OSNs. OSNs that express ORs (odorant receptor) are present in basiconic and trichoid sensilla and coeloconic sensilla house IR expressing OSNs. (b) Schematic view of insect ORs formed by heptahelical OrX and Orco (co-receptor) proteins. The second intracellular loop of Orco contains the highly conserved CaM binding site 336SAIKYWVER344. (c) GCaMP labelled fluorescence intensity of OrX/Orco expressing OSNs. (d) Time course of Ca2+ fluorescence responses obtained in OrcoWT OSNs and OrcoK339N OSNs upon ORs stimulation with 100 µM VUAA1 (n = 10 for OrcoWT, n = 11 for OrcoK339N). (e) Concentration response relationship for OrcoWT and OrcoK339N (7 ≤ n ≤ 11). Curves represent sigmoidal fits described by Hill coefficient 1.44 (OrcoWT) and 0.89 (OrcoK339N), and EC50 of 88 µM (OrcoWT), 85 µM (OrcoK339N). (f) Maximum fluorescence response (Max ∆F/F0 (%)) obtained by subtracting the base level at 50 s from the maximum Ca2+ fluorescence at 1 mM VUAA1. n = number of antennae. Two-tailed unpaired t- test, **P < 0.01. Data given as mean ± SEM. Scale bar of antenna: 20 µm.
