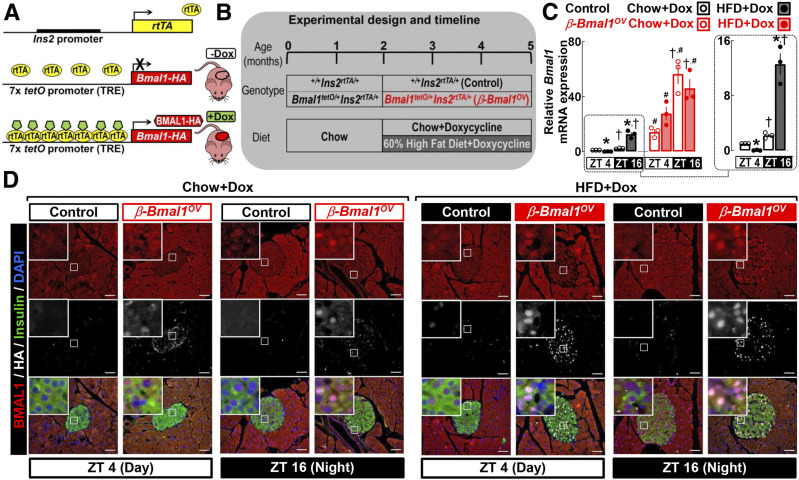
Figure 1.
Generation and validation of β-cell Bmal1 overexpression in male mice. A and B: We generated mice with conditional β-cell–specific expression of Bmal1 by crossing mice expressing HA copy of Bmal1 under the control of tetO promoter (tetO-Bmal1-HA) with mice expressing the rtTA under the control of rat insulin promoter (Ins2-rtTA). Resultant offspring and corresponding controls were exposed to either chow or 60% HFD, while Bmal1 expression was driven by provision of DOX in food. C: Normalized Bmal1 mRNA from islet lysates of chow- and HFD-fed control (+/+Ins2rtTA/+) and β-Bmal1OV (Bmal1-HAtetO/+Ins2rtTA/+) male mice collected at the ZT 4 and ZT 16 time points. Data are mean ± SEM (at least n = 3 mice per genotype/diet) fold change, with chow-fed control at ZT 4 set as 1. Statistical significance was determined by three-way ANOVA for effects of genotype, diet, and ZT with post hoc multiple comparison analysis. *P < 0.05 for chow vs. HFD; #P < 0.05 for control vs. β-Bmal1OV; †P < 0.05 for ZT 4 vs. ZT 16. D: Representative pancreatic sections stained by immunofluorescence for BMAL1, insulin, and HA and counterstained with nuclear marker DAPI imaged at 20× (scale bars = 50 μm) and magnification ×63 (insets) in chow- and HFD-fed control and β-Bmal1OV mice at the ZT 4 and ZT 16 time points. In total, representative pancreatic specimens from at least n = 3 mice per genotype/diet were examined.