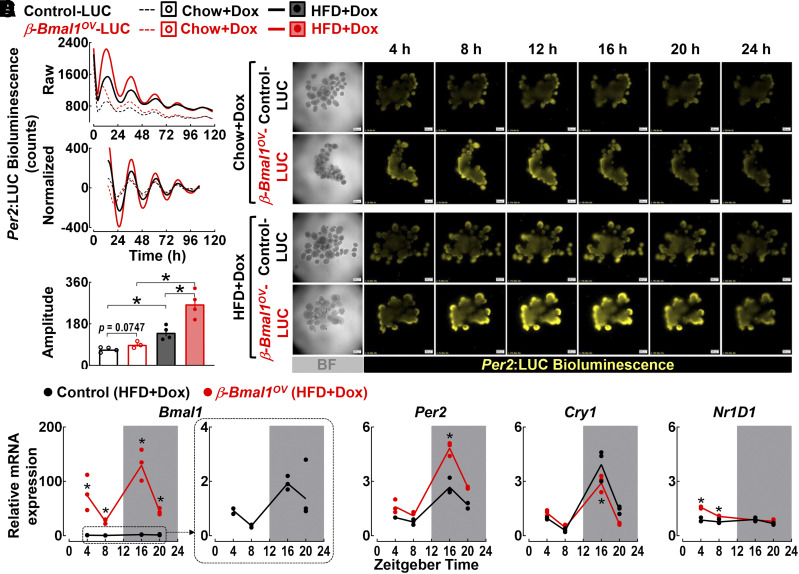
Figure 3.
β-Cell Bmal1 overexpression enhances islet circadian clock amplitude in Per2:LUC reporter male mice. A: Representative examples of Per2-driven bioluminescence rhythms (raw and normalized counts). B: Twenty-four hours of time-lapse microscopy recordings in islets isolated from control-LUC (+/+Ins2rTtA/+Per2luc/+) and β-Bmal1OV-LUC (Bmal1-HAtetO/+Ins2rTtA/+Per2luc/+) mice exposed to either chow or HFD (scale bars = 200 μm). C: Mean circadian amplitude of Per2-driven bioluminescence rhythms in islets of chow or HFD-fed control (+/+Ins2rTtA/+Per2luc/+) and β-Bmal1OV (Bmal1-HAtetO/+Ins2rTtA/+Per2luc/+) mice. Raw bioluminescence data were normalized by subtraction of the 24-h running average and then smoothed with a 2-h running average. Note that the first 12 h of raw counts are not included in the normalized data. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3–4 independent experimental repetitions per genotype/diet using isolated islets from n = 2 mice per genotype/diet). *P < 0.05. D: Bmal1, Per2, Cry1, and Nr1d1 mRNA levels obtained from islet lysates of HFD-fed control (+/+Ins2rtTA/+) and β-Bmal1OV (Bmal1-HAtetO/+Ins2rtTA/+) male mice collected at the ZT 4, 8, 16, and 20 time points in the 24-h circadian cycle. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3 independent experimental repetitions per ZT/genotype using isolated islets from n = 2–4 mice per ZT/genotype) fold change, with control at ZT 4 set as 1. *P < 0.05 vs. control (two-way ANOVA). BF, bright field.