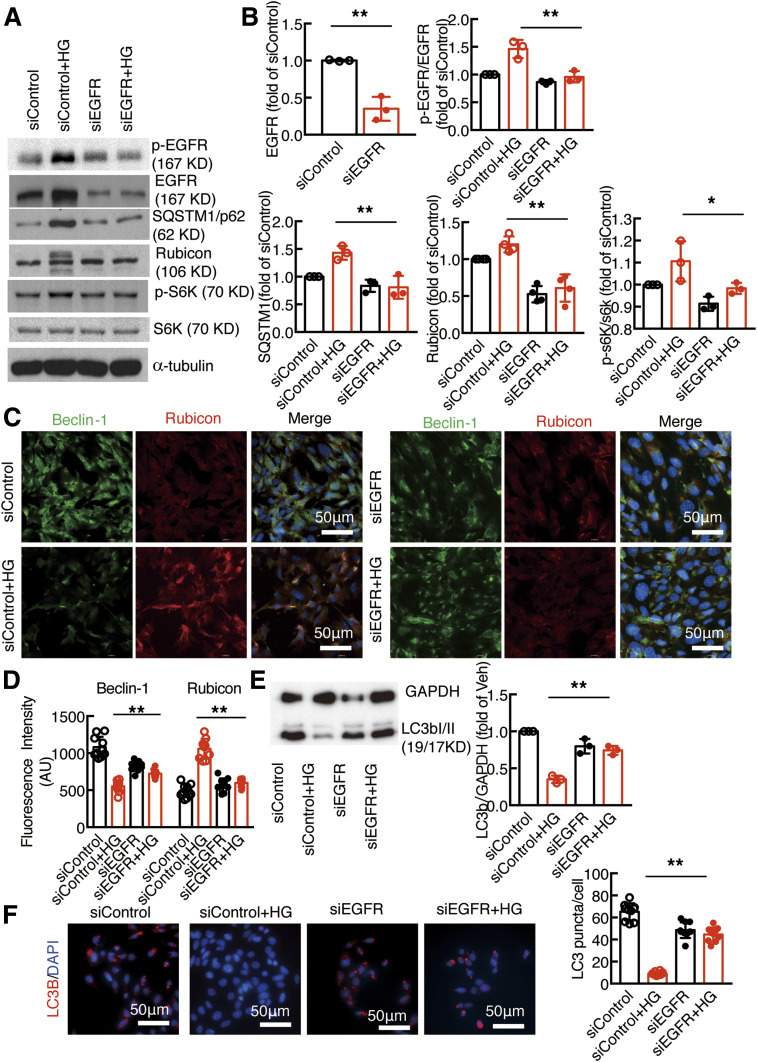
Figure 2.
Knockdown of EGFR attenuated increased rubicon expression and promoted autophagic flux in cultured podocytes. A and B: siRNA knockdown of podocyte EGFR led to less activation of EGFR signaling and decreased SQSTM1, rubicon, and phosphorylated (p-)S6K expression. C and D: High glucose–induced beclin-1 inhibition and rubicon stimulation in podocytes were abolished by siEGFR. E and F: siRNA knockdown of podocyte EGFR increased LC3B abundance after exposure to high glucose compared with control siRNA, which promoted autophagosome production. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 vs. siControl group with high glucose (HG), N = 3 independent repeats, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test. AU, arbitrary units.