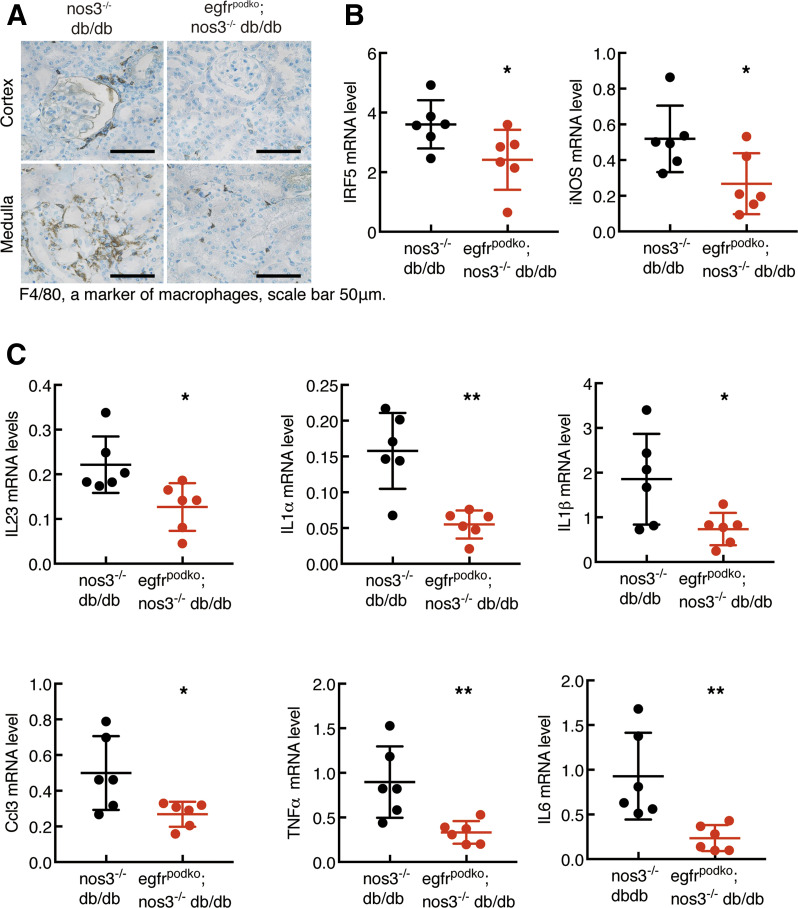
Figure 6.
Podocyte EGFR deficiency decreased renal macrophage infiltration and renal proinflammatory cytokines in nos3−/− db/db mice. Both egfrf/f; nos3−/−; db/db (nos3−/−; db/db) mice and nphs2-Cre; egfrf/f; nos3−/−; db/db (egfrpodKO; nos3−/−; db/db) mice were sacrificed at 20 weeks of age. A: EGFR deletion in podocytes led to decreased renal macrophage infiltration, as indicated by F4/80 staining, a marker of macrophages. Original magnification: ×400. B: EGFR deletion in podocytes decreased renal mRNA levels of IRF5, a transcription factor inducing macrophage M1 polarization, and NOS2, a marker of M1 macrophages. *P < 0.05, n = 6 in each group. C: EGFR deletion in podocytes led to decreased renal mRNA levels of proinflammatory cytokines/chemokines, including IL23, IL1α, IL1β, CCL3, TNFα, and IL6. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (n = 6 in each group), two-tailed unpaired Student t test.