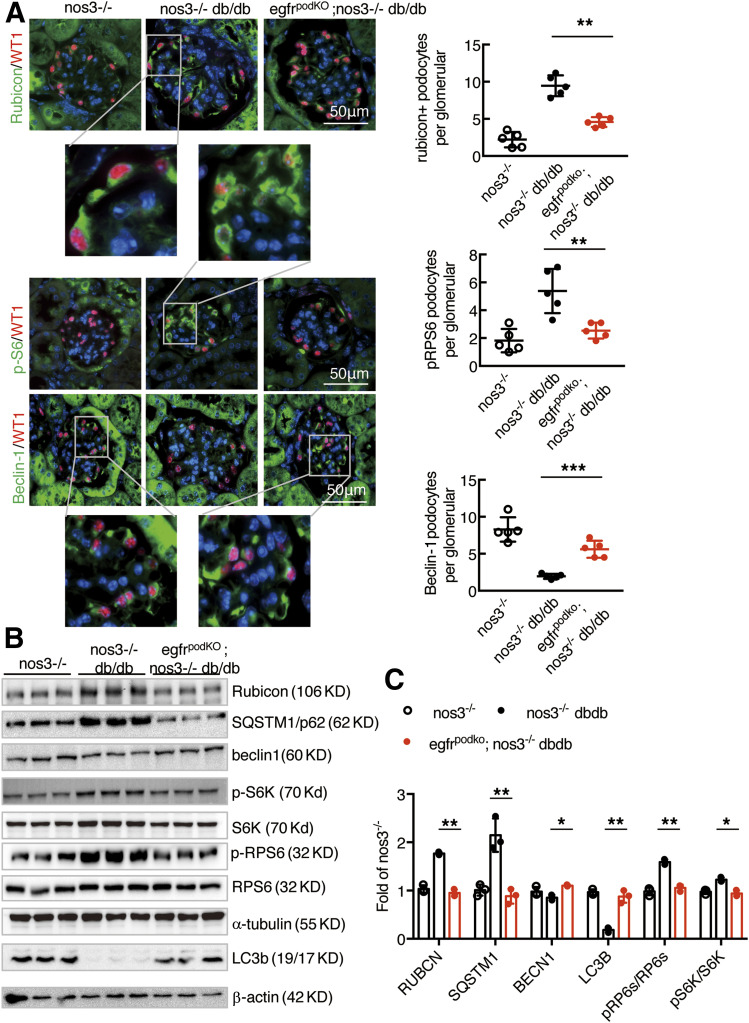
Figure 7.
Podocyte EGFR deficiency led to increased autophagy in podocytes in nos3−/− db/db mice. Both nos3−/−; db/db (nos3−/−; db/db) mice and nos3−/−; db/db (EgfrpodKO; nos3−/−; db/db) mice were sacrificed at 20 weeks old. A: Representative kidney sections were stained and indicated that podocyte EGFR deletion decreased rubicon, SQSTM1, and phosphorylated (p)RPS6 (Ser240/244) protein expression and increased renal beclin-1. Quantification for rubicon, pRPS6/RPS6, and beclin-1 (colocalized with WT1, a podocyte nucleus marker) glomerulus represents results from 30 glomeruli each from five mice. **P < 0.01. B and C: Western blot of glomerular lysates obtained from nos3−/−; db/db (nos3−/−; db/db) mice and nos3−/−; db/db (egfrpodKO; nos3−/−; db/db) mice for rubicon, beclin-1, phosphorylated RPS6/RPS6 protein expression, LC3B I/II turnover and SQSTM1 abundance. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, n = 3 in nos3−/− group, n = 3 in nos3−/−; db/db group, and n = 3 in egfrpodKO; nos3−/−; db/db group; one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test.