Figure 3. IntA to fentanyl is associated with increased number of orexin-immunoreactive neurons.
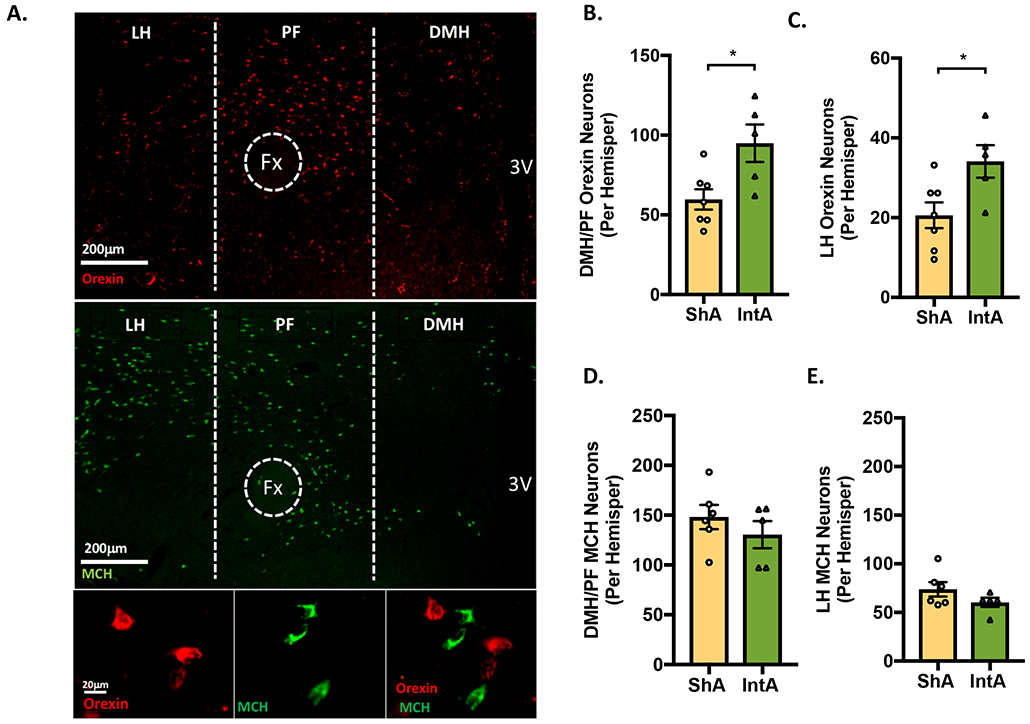
Orexin- and MCH-immunoreactive neuronal numbers were assessed after 90 days of abstinence in rats previously given ShA (n=7) or IntA (n=5) to fentanyl. A) Low magnification photomicrograph of a frontal section showing orexin (red; top panel) and MCH neurons (green; middle panel) in the hypothalamus of a rat given IntA to fentanyl. High-magnification photomicrograph showing orexin (red; bottom left), MCH (green; bottom middle), and merge (bottom right). B-C) Compared to ShA, rats given IntA to fentanyl had a greater number of orexin neurons in the both the DMH/PF and LH orexin cell fields [independent samples t-tests]. D-E) In contrast, the number of DMH/PF and LH MCH- neurons did not differ between ShA and IntA rats. For all panels, *p<0.05
