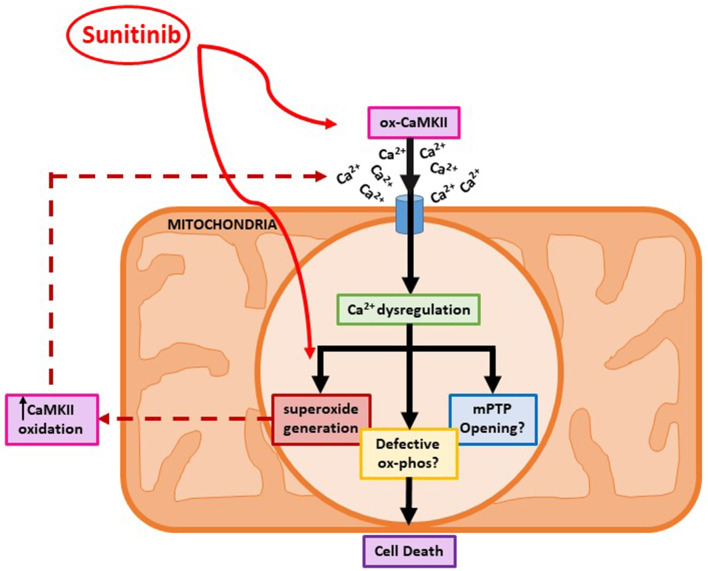
Figure 9.
A proposed mechanism for sunitinib-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in adult cardiac fibroblasts. Schematic showing proposed sunitinib-induced events at the level of the mitochondria in CFs. Sunitinib treatment may exert direct effects on mitochondrial superoxide production that can then result in CaMKII oxidation. Sunitinib-induced increases in CaMKII oxidation and activation can then go on to cause elevated superoxide production so a positive feedback loop may exist exacerbating the cardiotoxic effects. The combination of elevated CaMKII oxidation and increased superoxide production ultimately causes toxicity at the level of the mitochondria and can contribute to CF cell death.