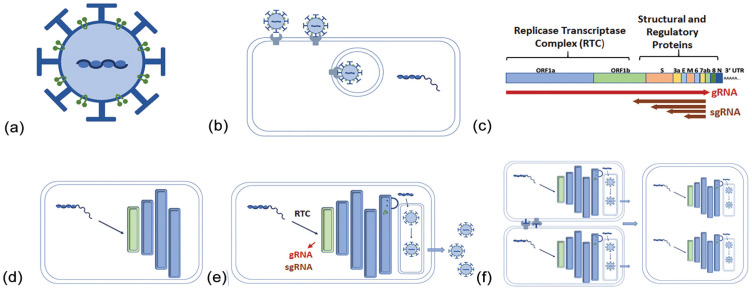
Figure 1.
Life cycle of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. (a) Spike ( ), envelope, and matrix (
), envelope, and matrix ( ) proteins are expressed on the surface of this single-stranded RNA virus. Nucleocapsid protein binds and protects the genomic RNA (gRNA) until (b) the virus enters the cells via spike protein interaction with cellular ACE2. (c) The gRNA of the positive-stranded RNA is transcribed and translated as a single ORF, yielding the RTC. Structural proteins are transcribed subsequently from the (subgenomic, sg) 5’ end of the gRNA. (d) The RTC integrates with the endoplasmic reticulum to form a double-membrane vesicle (DMV). (e) This structure produces virus which is released. (f) Local viral load leads to the formation of multinucleated giant cells through the binding of spike and ACE2 proteins on the surface of local cells. Abbreviations: SARS-CoV-2 = severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; ORF = open reading frame; RTC = replicase-transcriptase complex; ACE2 = angiotensin-converting enzyme 2.
) proteins are expressed on the surface of this single-stranded RNA virus. Nucleocapsid protein binds and protects the genomic RNA (gRNA) until (b) the virus enters the cells via spike protein interaction with cellular ACE2. (c) The gRNA of the positive-stranded RNA is transcribed and translated as a single ORF, yielding the RTC. Structural proteins are transcribed subsequently from the (subgenomic, sg) 5’ end of the gRNA. (d) The RTC integrates with the endoplasmic reticulum to form a double-membrane vesicle (DMV). (e) This structure produces virus which is released. (f) Local viral load leads to the formation of multinucleated giant cells through the binding of spike and ACE2 proteins on the surface of local cells. Abbreviations: SARS-CoV-2 = severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; ORF = open reading frame; RTC = replicase-transcriptase complex; ACE2 = angiotensin-converting enzyme 2.