Figure 6.
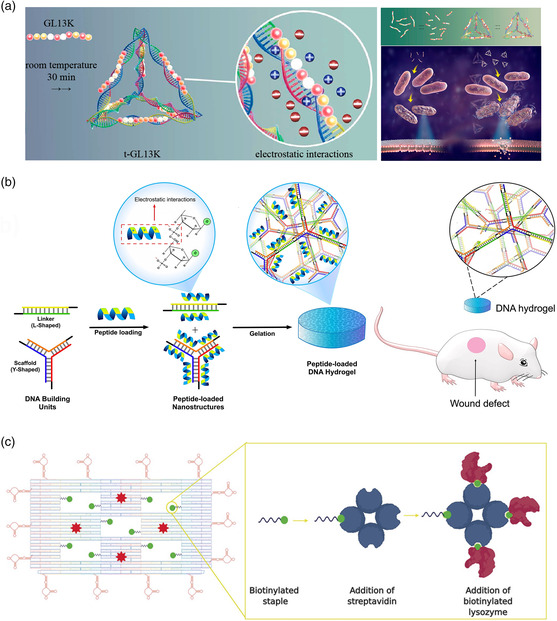
Transport of peptide‐ and enzyme‐based bactericidal substances. a) An AMP known to disrupt the membrane of several species of bacteria is electrostatically attached to the edges of a DNA tetrahedron. This leads to an enhanced antibacterial rate in species known to be susceptible as well as those that are previously shown to be resistant to the AMP. Reproduced with permission.[ 110 ] Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society. b) A DNA‐based hydrogel is loaded with a broad‐spectrum AMP and used as a wound dressing in in vivo experiments, reducing healing times. Reproduced with permission.[ 112 ] Copyright 2019, Elsevier B.V. c) A bactericidal enzyme, lysozyme, is loaded in high amounts onto a DNA origami nanostructure, together with aptamers that target specific Gram‐negative and Gram‐positive bacteria. Reproduced with permission.[ 115 ] Copyright 2020, John Wiley and Sons.
