Figure 1.
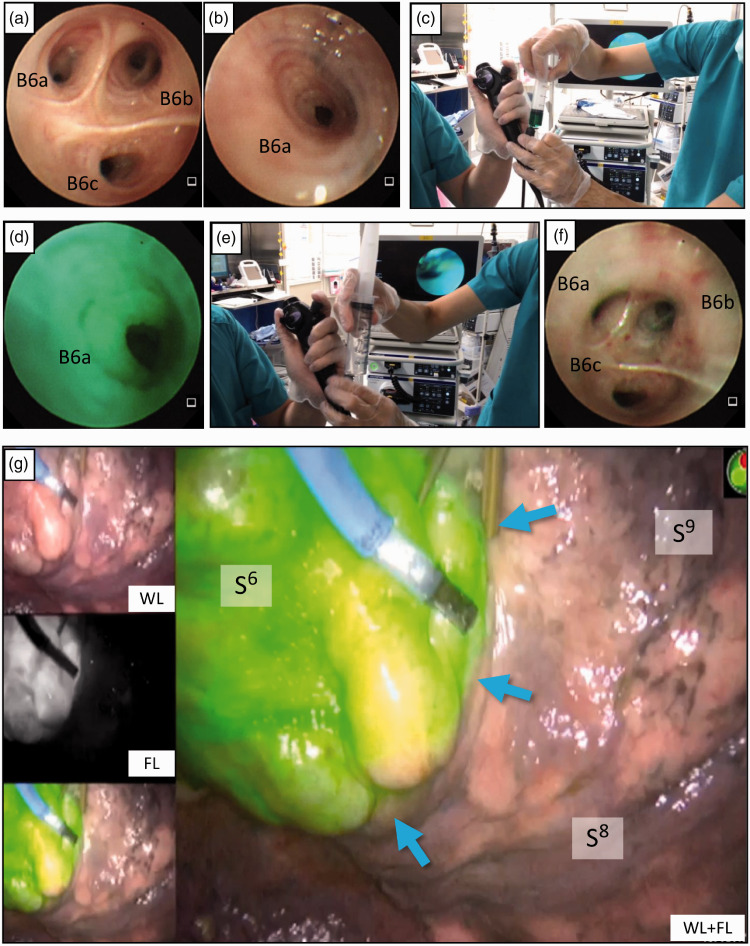
Indocyanine green (ICG)-fluorescence (FL) intersegmental plane visualization by bronchoscopic ICG insufflation. After inducing general anesthesia and endotracheal intubation, the bronchoscope is advanced to the targeted segmental bronchus. (a) Bronchoscopic view of left subsegmental bronchus B6a, B6b, and B6c before ICG insufflation. (b) The orifice of the left B6a wedged by the tip of the flexible bronchoscope before ICG insufflation. (c) A bolus of ICG (0.0125 mg/mL) is insufflated into each subsegmental bronchus through the bronchoscope’s utility channel. (d) Bronchoscopic view of B6a during ICG insufflation. (e) Immediately following the ICG bolus, 150 mL or more of air is pushed into the bronchus. (f) Bronchoscopic view of the left B6 after ICG insufflation into B6a, B6b, and B6c. (g) Subsequent video-assisted thoracoscopy showing that the left S6 segmental lung exhibits uniform ICG-FL, and the intersegmental plane (blue arrows) between S6 and S8 is visualized.
WL, white light-only image; FL, fluorescence-only image; Cr, cranial; Ca, caudal; Ve, ventral; Do, dorsal.