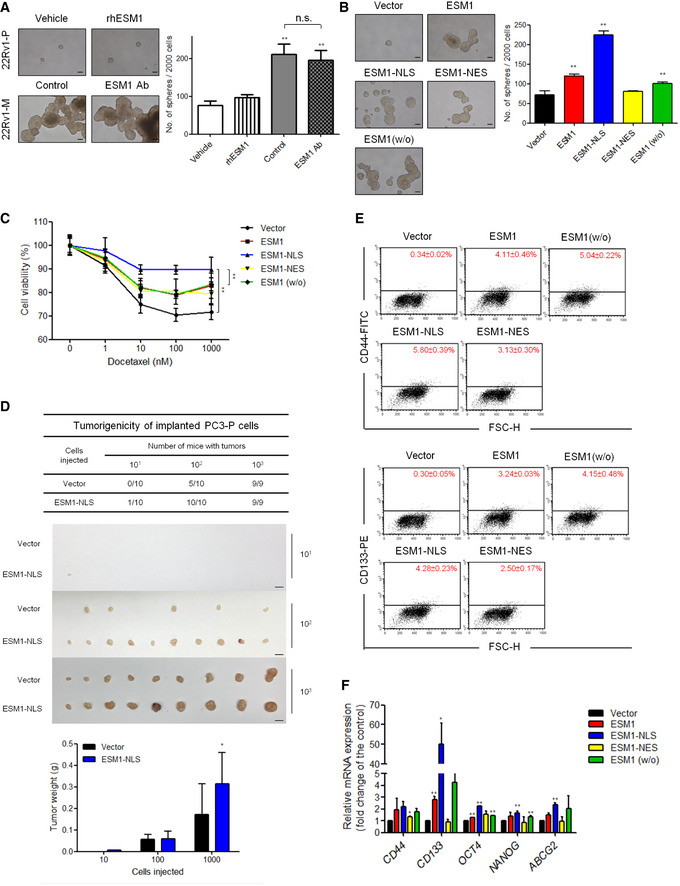
Tumor spheroid formation. Representative images of tumorspheres formed and quantitative data comparing the average number of spheres formed in the indicated cells treated with PBS or human recombinant ESM1 (rhESM1) or normal goat IgG control or anti‐ESM1 neutralizing antibody. Scale bar: 100 μm. Bars are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. **P < 0.01 when compared to the vehicle group of 22Rv1‐P cells by two‐tailed Student’s t‐test.
Representative images of tumorspheres. Spheres were cultured for 14 days before counting. Histogram shows the mean numbers of spheres cultured. Scale bar: 100 μm. Bars are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. **P < 0.01 when compared to vector cells by two‐tailed Student’s t‐test.
22Rv1‐P cells stably expressing ESM1 were treated with docetaxel at the indicated concentrations for 48 h. **P < 0.01 when compared to vector cells by two‐tailed Student’s t‐test and error bars represent the standard deviation of three independent experiments.
Cells with or without ESM1‐NLS overexpression were subcutaneously injected (10, 100, 1,000 cells per mouse) into NOD/SCID mice. Tumor formation ability and tumor weight were analyzed. Scale bar: 1 cm. Bars are the mean ± SD of indicated (n) independent experiments. *P < 0.05 when compared to vector cells by two‐tailed Student’s t‐test.
Flow cytometry analysis of the ratio of CD44+ and CD133+ cells in the indicated cells with different subcellular localization types of ESM1 overexpression was performed.
qRT–PCR analysis of the mRNA levels of the indicated genes in cells with different types of ESM1 overexpression. Differences in mRNA levels compared with vector cells are shown as fold changes presented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 when compared to vector cells by two‐tailed Student’s t‐test.