Figure 1. A CRISPR/Cas9 knockout screen identifies novel genes that arrest the proliferation of cells with centrosome amplification.
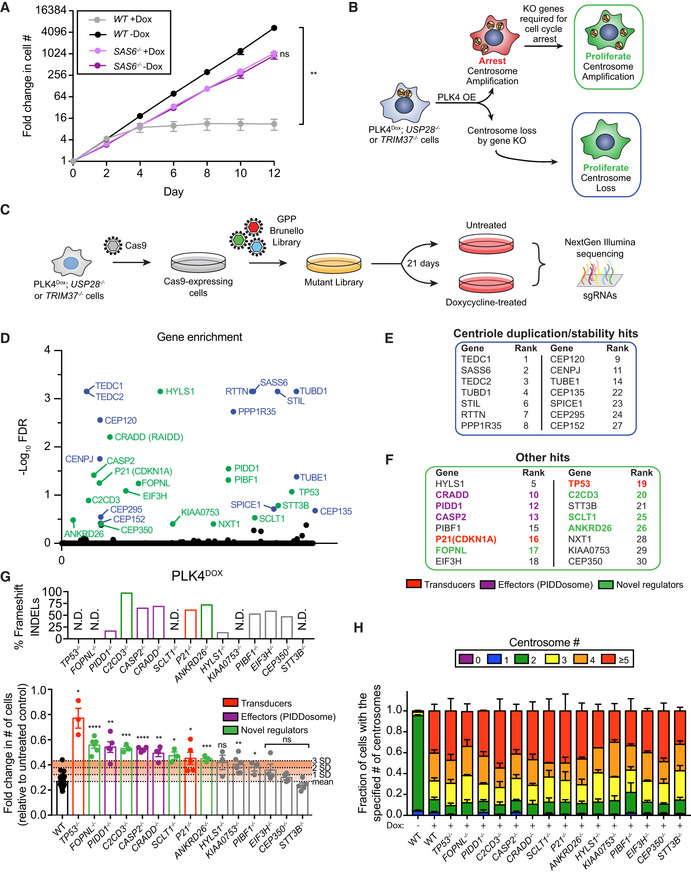
- Growth assay of the indicated cells with and with out doxycycline‐inducible overexpression of PLK4. Experiments were performed in wild‐type or SAS6 monoclonal knockout cells. Data acquired across n = 3 biological replicates. Mean ± s.e.m.
- Schematic overview of the screen design.
- Schematic showing the procedure for a CRISPR/Cas9‐positive selection screen to identify gene knockouts that increase the proliferation of cells with extra centrosomes.
- Top hits that emerged from the screens ranked by MaGeCK FDR value. Blue hits are genes required for centriole duplication or stability. Green hits are genes predicted to be required to arrest the growth of cells with extra centrosomes.
- Hits with a known role in centriole duplication or stability.
- Candidate hits responsible for arresting the proliferation of cells with centrosome amplification. Purple hits correspond to PIDDosome genes. Red hits correspond to downstream effectors. Green hits are novel regulators.
- Top: Graph showing the efficiency of frameshifting INDELs measured using TIDE. N.D. = Not determined. Data shown are from n = 1 biological replicate. Bottom: Graph showing the relative growth of doxycycline‐treated PLK4Dox cells expressing an sgRNA targeting the indicated genes. Each dot displays measurements from a single experiment. Experiments were performed in polyclonal knockout cells. Data acquired across n ≥ 3 biological replicates. Mean ± s.e.m.
- Quantification of centrosome number in PLK4Dox cells expressing an sgRNA targeting the indicated genes. Experiments were performed in polyclonal knockout cells. Data acquired across n ≥ 3 biological replicates. Mean ± s.e.m.
Data information: Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences between measurements (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001). Statistics for all Figures were calculated using a two‐tailed Student’s t‐test.
Source data are available online for this figure.
