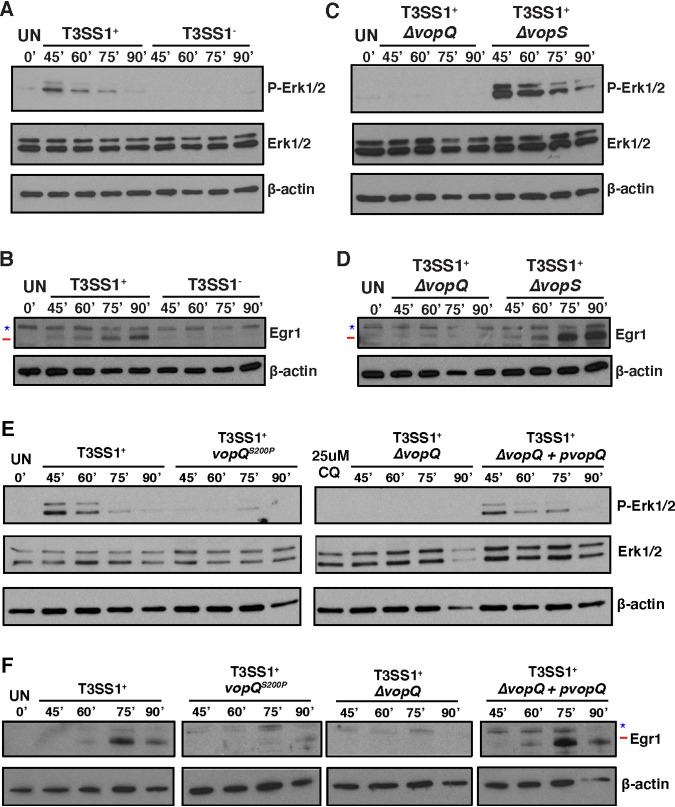
FIG 2.
VopQ but not VopQS200P induces an early activation of ERK1/2 MAPK signaling. (A) Immunoblot showing phosphorylated Erk1 and Erk2 (p-Erk1/2) and total Erk1/2 in starved mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) 45, 60, 75, and 90 min after infection with T3SS1+ or T3SS1− V. parahaemolyticus. A pulse of p-Erk1/2 was observed early during infection with T3SS1+ but not T3SS1− V. parahaemolyticus. (B) Immunoblot for total Egr1 in starved MEFs 45, 60, 75, and 90 min after infection with POR3:T3SS1+ or POR3:T3SS1−. A rise in Egr1 protein levels over time was observed only in T3SS1+-infected MEFs. (C) Immunoblot for p-Erk1/2 and total Erk1/2 in starved MEFs 45, 60, 75, and 90 min after infection with T3SS1+ΔvopQ or T3SS1+ΔvopS V. parahaemolyticus. T3SS1+ΔvopQ did not induce Erk1/2 phosphorylation while T3SS1+ΔvopS induced prolonged Erk1/2 phosphorylation. (D) Immunoblot for total Egr1 in starved MEFs 45, 60, 75, and 90 min after infection with V. parahaemolyticus T3SS1+ΔvopQ or T3SS1+ΔvopS. No rise in Egr1 protein levels was observed in T3SS1+ΔvopQ-infected MEFs, while T3SS1+ΔvopS caused an increase in Egr1 protein levels. (E) Immunoblot showing p-Erk1/2 and total Erk1/2 in starved MEFs infected with T3SS1+, T3SS1+vopQS200P, T3SS1+ΔvopQ, and T3SS1+ΔvopQ+pvopQ V. parahaemolyticus strains for 45, 60, 75, and 90 min. No pulse of pERK1/2 was observed in T3SS1+vopQS200P-infected MEFs. (F) Immunoblot for total Egr1 in starved MEFs infected for 45, 60, 75, and 90 min with the same V. parahaemolyticus strains as in panel E. T3SS1+vopQS200P did not trigger an increase Egr1 protein levels in infected MEFs. In panels B, D, and F, the target band is marked with a red line, and background bands are indicated with a blue star. Blots are representative of 3 independent experiments.