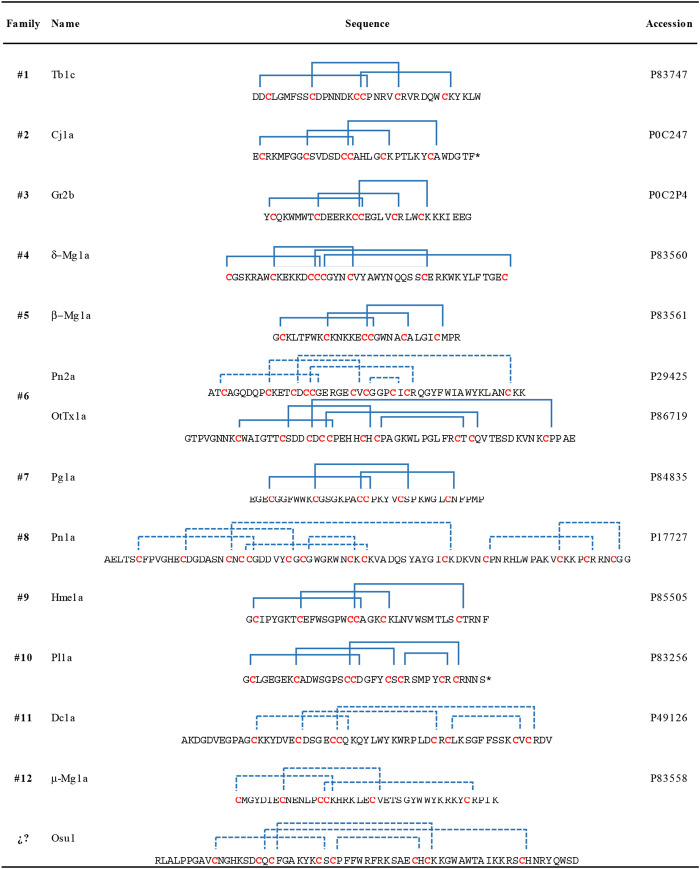
FIGURE 7.
Amino acid sequences and disulfide pairing of a representative member of the proposed families of spider sodium channel toxins, according to Klint et al. (2012) including the proposed primary structure and possible disulfide pairing in Osu1 as a new member of spider toxins. A primary structure of a representative member of each family is shown. Disulfide bridges are colored blue, and blue dotted lines represent predicted disulfide bond connectivities that have not been experimentally validated. Asterisks at the C-terminal mean C-amidation. Here our intention is not to propose Osu1 as new Nav spider toxin, but to use the Klint et al. spiders’ toxin classification to show the novelty of the amino acid sequence between Cys residues, and the possible disulfide-pairing motif of Osu1. Toxin names are based on the rational nomenclature devised for spider-venom peptides (King et al., 2008).