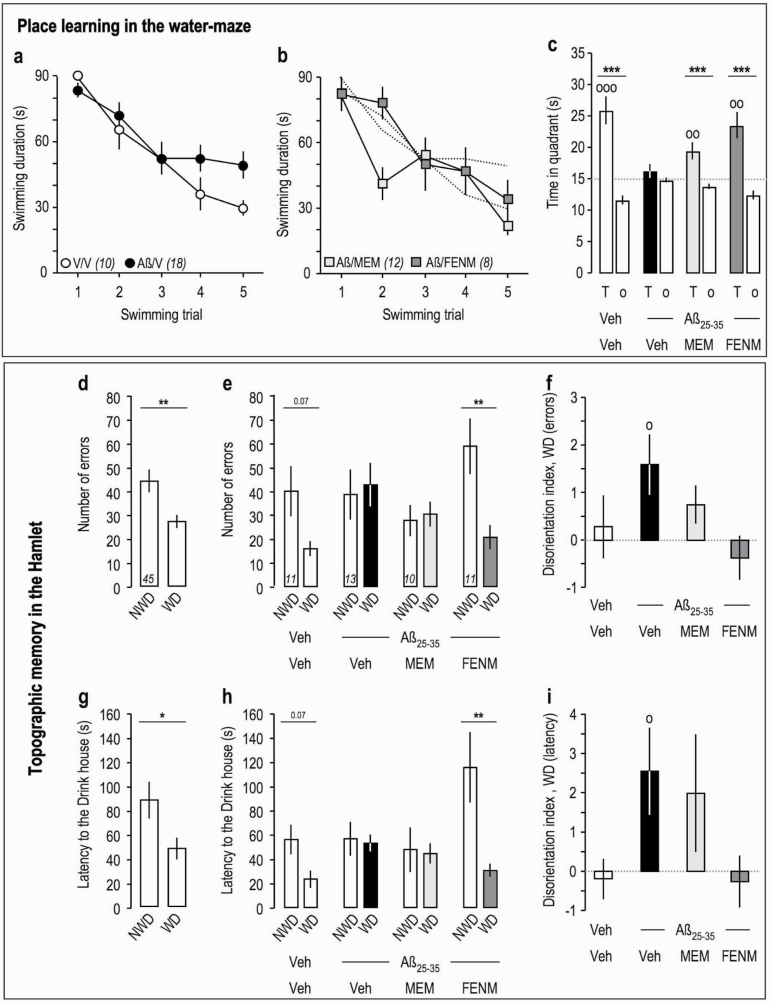
Figure 2.
Effects of Memantine and FENM administered at 0.3 mg/kg IP on Aβ 25-35-induced learning impairments: (a–c) spatial reference memory in the water-maze in mice; (d–i) topographic memory in the Hamlet test. (a) Acquisition of Veh-treated and Aβ 25-35-injected animals. (b) Acquisition of animals receiving Memantine or FENM, 0.3 mg/kg IP, 30 minutes before the training trials sessions (anti-amnesia). (c) Time spent in the training (T) or the others (o) quadrants for each experimental group. °°P < .01, °°°P < .001 vs 15 seconds; 1-sample t test; ***P < .001 vs o quadrants; Student’s t test. Hamlet probe test data were analyzed in terms of errors (d–f) and latencies (g–i) to reach the Drink house. (d, g) Probe test performed 72 hours after Hamlet training. (e, h) Probe test performed 1 week after the ICV injection of Aβ 25–35 and 30 minutes after IP injection of Memantine or FENM. (f, i) Disorientation index calculations for errors (f) or latencies (i). *P < .05, **P < .01 vs non-water deprived, paired t test; °P < .05 vs zero level, 1-sample t test.