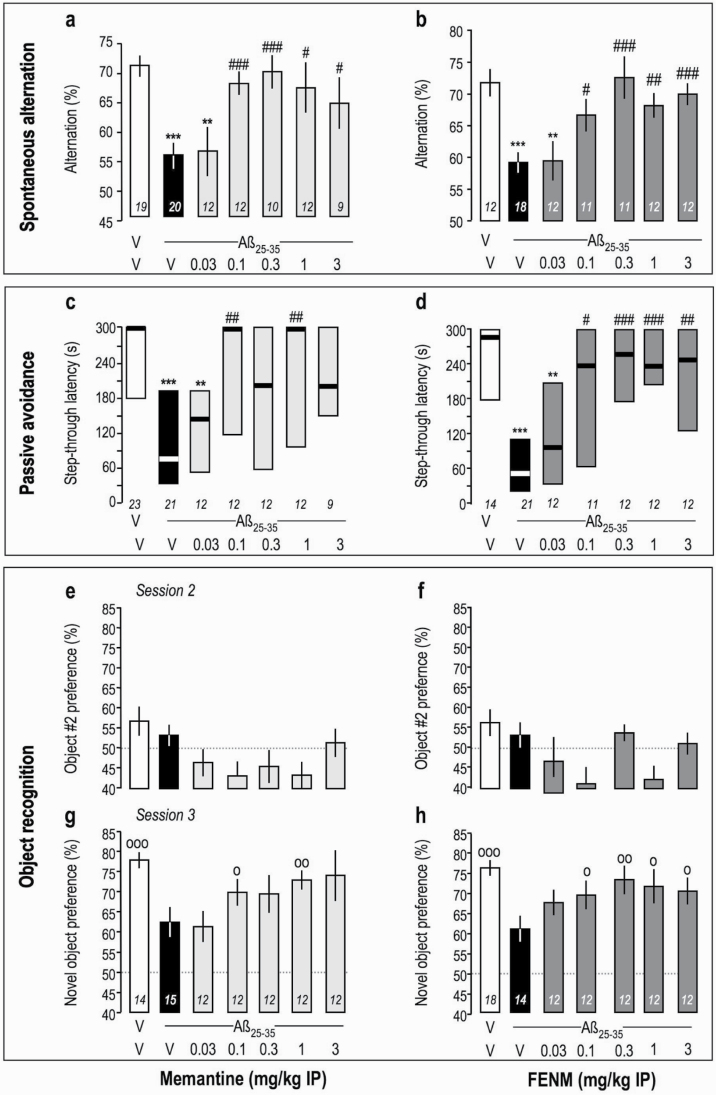
Figure 3.
Protective effect of Memantine (a, c, e, g) and FENM (b, d, f, h), administered IP, on Aβ 25-35-induced learning impairments in mice: (a–b) spontaneous alternation performance, (c–d) passive avoidance, and (e–h) object recognition tests. Animals received Memantine or FENM (0.1–10 mg/kg i.p.) o.d. between day 1 to 7 and injections stopped 24 hours before the first behavioral session. For the object recognition test, exploration preferences are calculated with the duration of contacts in session 2, with 2 identical objects (e–f) and in session 3 with a novel object (g–h). Data show mean ± SEM (a, b, e–h) and median and interquartile range (c–d). ANOVA: F(6,93) = 5.16, P < .0001 (a); F(6,90) = 6.21, P < .0001 (b). Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA: H = 21.6, P < .01 (c); H = 29.8, P < .001 (d). *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001 vs (V+V)-treated group; #P < .05, ##P < .01 vs (V+Aβ 25–35)-treated group; Dunnett’s test (a–b), Dunn’s test (c–d). °P < .05, °°P < .01, °°°P < .001 vs 50% level, 1-sample t test (g–h).