FIGURE 5.
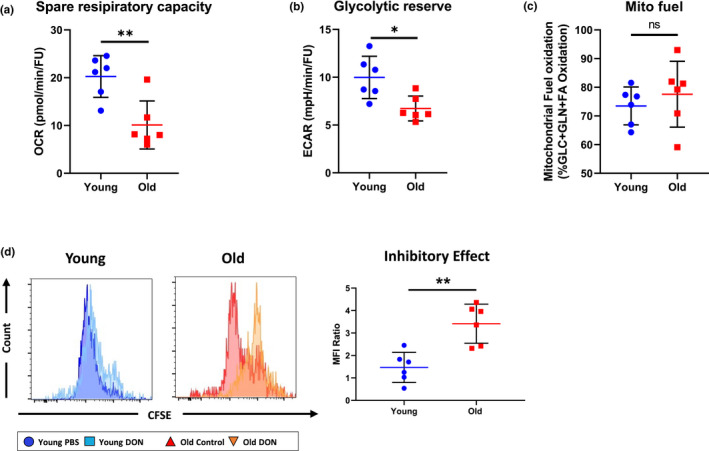
DON inhibits human CD4+ T‐cell age specifically. (a and b) Naïve human CD4+ T cells were isolated from young and old healthy volunteers and activated with 10 µg/ml anti‐CD3 and 2 µg/ml soluble anti‐CD28 for 24 h. Calculated spare respiratory capacity and glycolytic reserve were assessed utilizing a Seahorse Mito Stress. (c) Dependence for mitochondrial fuel on distinct metabolic pathways of young and old naïve human CD4+ T cells 24 h of activation is shown. (d) Naïve CD4+ T cells were isolated from young and old healthy volunteers, cultured in a mixed lymphocyte reaction to which either PBS or DON had been added and labeled with CFSE. After 72 h, proliferation of naïve CD4+ T cells was measured by the dilution of CFSE and the inhibitory effects of DON measured by the ratio of CFSE median fluorescence intensity between the DON and the PBS group. Column plots display individual data points and mean ± SD, n = 5/group. Statistical significance was determined by using Mann–Whitney test. Asterisks indicate p‐values *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, and ***p ≤ 0.001, only significant values are shown. The results are representative of at least three independent experiments
