FIGURE 1.
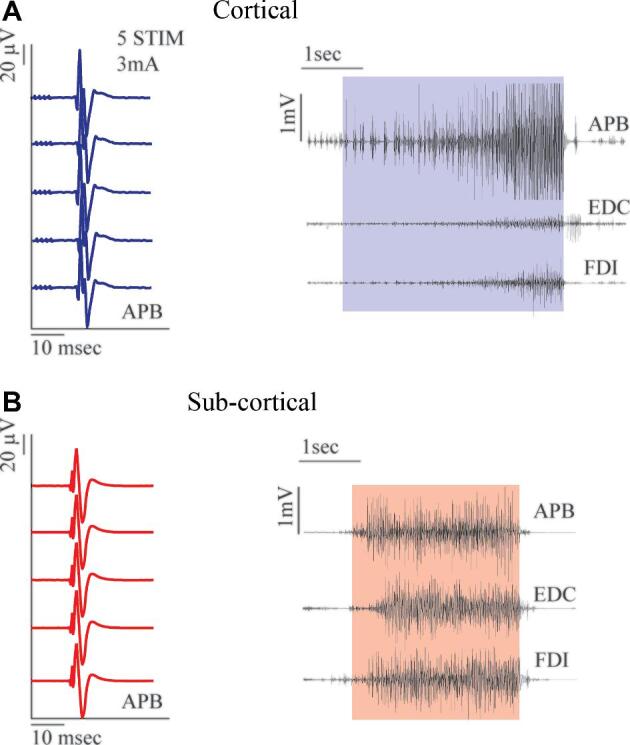
A, Left panel: Asleep surgery HF stimulation (4 mA, 5 pulses, 0.5-ms duration, 4-ms ISI, 1-Hz repetition rate, anodal, monopolar probe) on the primary motor cortex-hand knob region recruits MEPs in APB. Right panel: Asleep surgery LF stimulation (bipolar probe, 60 Hz, 4 mA) over the same hand-knob region of the primary motor cortex at threshold intensity evokes the somatotopic recruitment of different hand muscles (APB, EDC, FDI). The electrically induced EMG activity shows a progressive recruitment of motor units from the onset towards the end of the stimulus. B, Left panel: Asleep surgery. MEPs obtained in hand muscles (APB) by HF stimulation of the CST on the subcortical level (3 mA, 5 pulses, 0.5-ms duration, 4-ms ISI, 1-Hz repetition rate, cathodal, monopolar probe). Right panel: Asleep surgery LF subcortical stimulation (bipolar probe, 60 Hz, 6 mA). The EMG recruitment of different hand muscles (APB, EDC, FDI) is characterized by a tonic waveform. APB = abductor pollicis brevis, EDC = extensor digitorum communis, FDI = first dorsal interosseus.
