Figure 1.
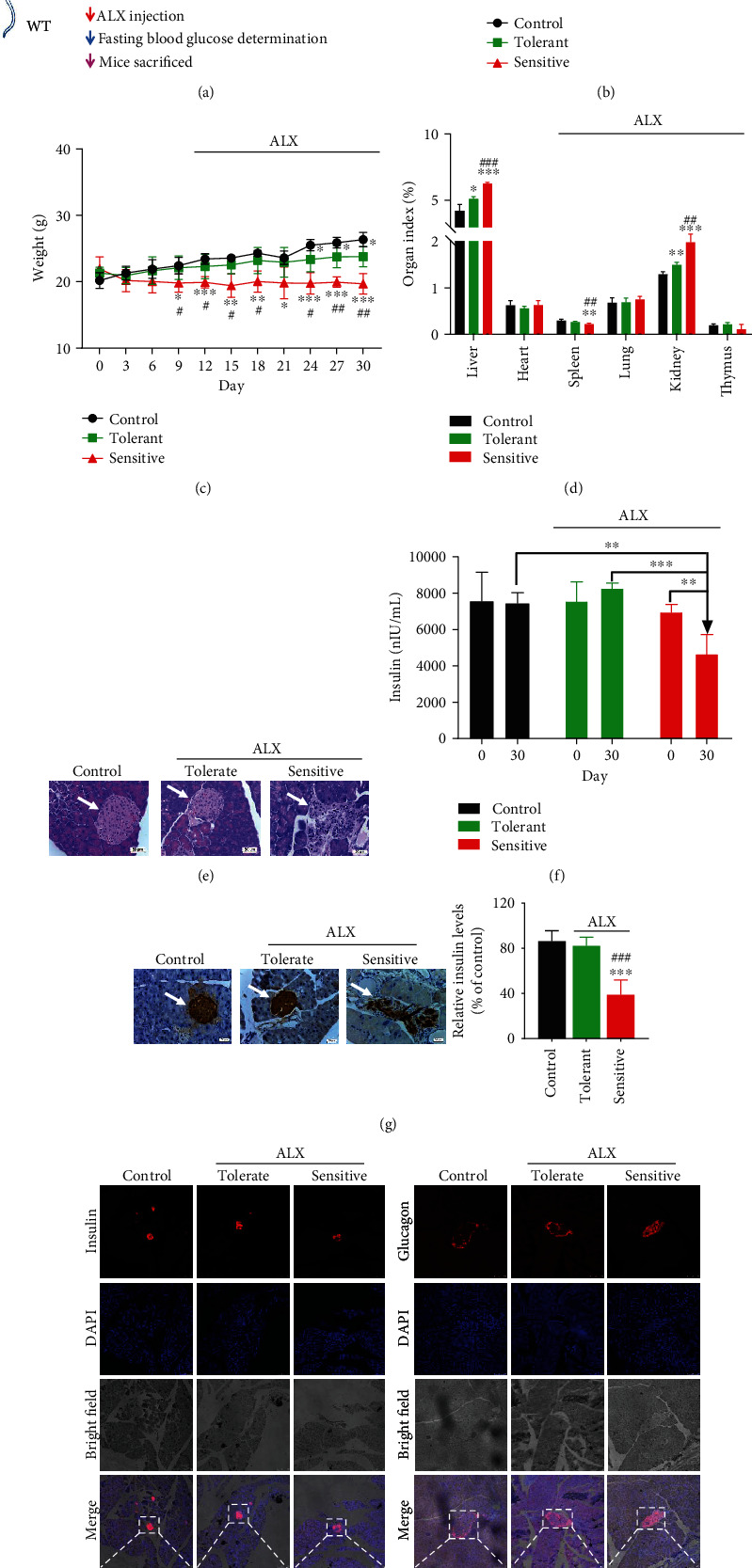
The susceptibility to ALX-induced T1DM varies significantly among different individuals of WT C57BL/6J mice. (a) A stimulated T1DM animal model in WT C57BL/6J mice was established by injection with ALX (60 mg/kg body weight) via the tail vein after 24 hours of fasting. The fasting blood glucose concentrations and body weights were measured every three days for one month. (b) Average blood glucose concentration curves for the mice. (c) Average body weight curves for the mice. (d) Organ indexes for mouse livers, hearts, spleens, lungs, kidneys, and thymuses. (e) Representative images showing hematoxylin and eosin staining of pancreatic islets for the mice. (f) The insulin concentrations in mouse plasma were assessed by using an ELISA Kit. (g) The insulin in the pancreatic islets of the mice was detected by immunohistochemistry. (h) The insulin and glucagon in the pancreatic islets of the mice were detected by immunofluorescence. The data represent the mean ± SD (n = 5). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001 compared with the control group; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, and ###p < 0.001 compared with the tolerant group.
