Figure 4.
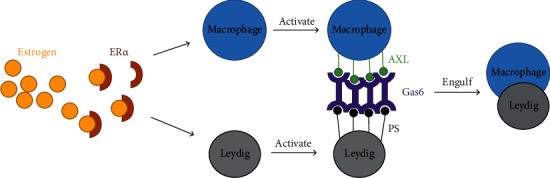
Mechanism of the estrogen-induced phagocytosis of Leydig cells by macrophages. Estrogen acts on macrophages and Leydig cells through estrogen receptor ER. In Leydig cells, estrogen activates its cell surface overexpression of phospholipid amino acid, PS, and growth specificity gene 6, Gas6. Through the Gas6, the PS molecules bind to AXL, one of the TAM receptor tyrosine kinase subfamily, which are overexpressed by macrophages after the estrogen stimulation. Namely, the PS molecules are an “eat me” signal to attract the macrophage cell to engulf the Leydig cells.
