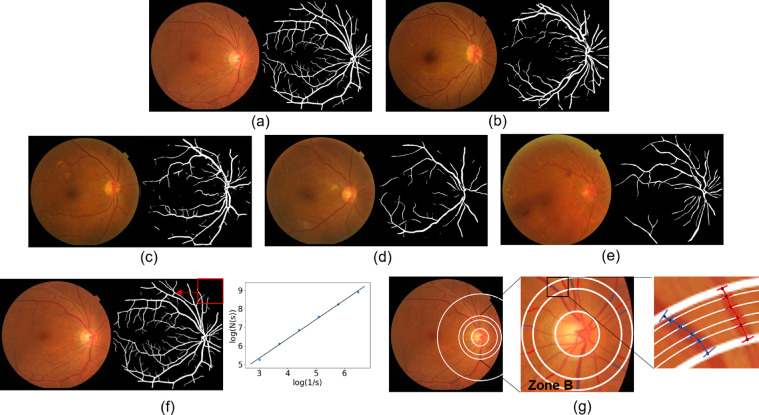
Figure 1.
Automatic segmentation and quantitative measurement of retinal vessels. (a) The retinal vessel segmentation results in healthy eyes, (b) mild DR, (c) moderate DR, (d) severe NPDR, (e) proliferative retinopathy, and (f) the quantitative calculation of Df. Each segmented mask was divided into a series of squares by sliding windows, s represents the relative value of the window width to the image width, N(s) is the number of squares that contain blood vessels. Adjust the value of s to get multiple groups (s, N(s)), Df was then defined as the gradient of logarithms of the number of squares and the size of those squares; (g) is the measurement principle diagram of vessel caliber biomarkers. Zone B is defined as an area of 0.50 to 0.75 disc diameter surrounding the optic disc, all arterioles (red lines) and venules (blue lines) coursing through zone B were measured, 6 vessel diameters were obtained at different locations for each vessel and then the Knudtson–Hubbard formula was used to calculate average retinal arteriolar and venular caliber.