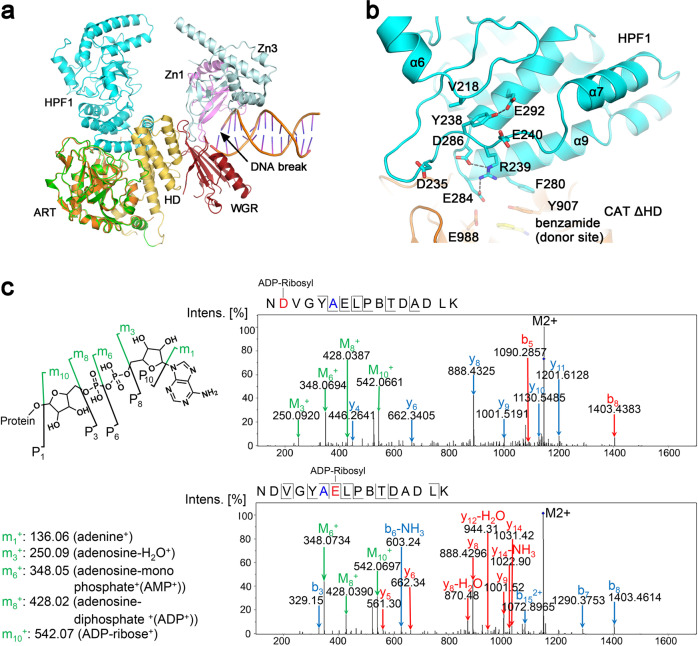
Fig. 4. Depicting the function of HPF1 Arg239.
a Comparison of the HPF1/PAPR1-CAT ΔHD complex structure and the DNA-bound PARP1 crystal structure (PDB 4DQY)18 by superimposing the ART domains from both (orange—ART determined in this report; green—ART of PDB 4DQY). HPF1 binding to PARP1 would presumably dislodge PARP1 automodification domain (AD) that was previously proposed to be located roughly in the same position where HPF1 binds (see Supplementary Fig. 1), thus prevents automodification of PARP1. b A close view of the long α6-α7 loop region structure and its position relative to the active center of the HPF1/PARP1 complex. c Mass Spectrometry analysis revealed that HPF1 R239A mutation resulted in ADP-ribosylation on Asp235 and Glu240, a unique phenomenon only seen in this mutant (see Fig. 2B, black arrow). The mutated residue 239 is shown in blue in the sequence, while the modified residues Asp235 and Glu240 are shown in red.