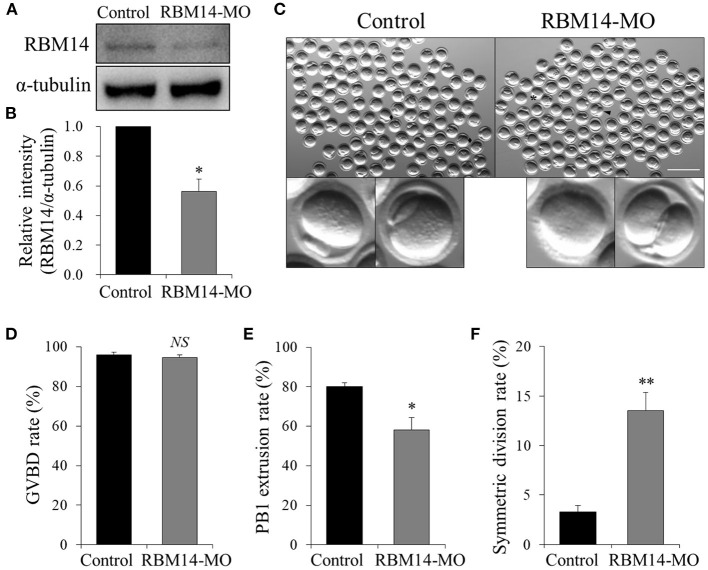
Figure 3.
Effects of RBM14 MO on the maturation of mouse oocytes. (A) Western blot analysis verified the efficiency of endogenous RBM14 knockdown. (B) RBM14 band intensities normalized to α-tubulin. (C) Representative bright-field images of RBM14-MO injected and control oocytes. Black rhombuses: successful polar body extrusion in control oocytes; black arrow: oocyte with apparent symmetric division; black asterisk: oocyte failed to extrude a polar body. Scale bar = 200 μm. (D) Rate of GVBD in control and RBM14-MO injected oocytes. (E) Rate of polar body extrusion in control and RBM14-MO injected oocytes. (F) Rate of symmetric division in control and RBM14-MO injected oocytes. A total of 364 control oocytes and 332 RBM14-MO injected oocytes were analyzed. Data are mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. NS, not significant, *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01.