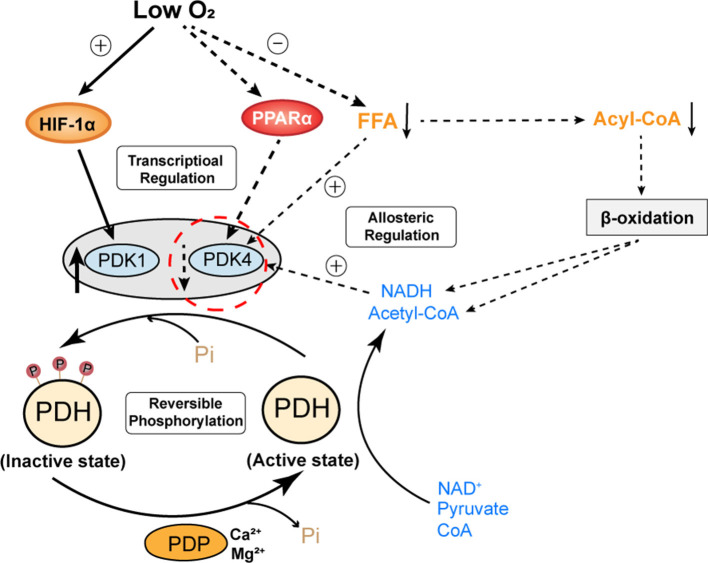
Figure 3.
A proposed regulation model of cardiac PDH activity under chronic hypoxia. The activity of PDH is mainly determined by reversible phosphorylation from PDK and PDP. PDK1 is oxygen sensitive and transcriptionally regulated by HIF-1α. PDK4 is nutrient sensitive, its expression is transcriptionally regulated by PPARα and its activity is allosterically regulated by FFA and metabolites (NADH, acetyl-CoA) derived from the oxidation of pyruvate or FFA. Under chronic hypoxia, elevated HIF-1α and decreased PPARα have opposing effects on the expression of PDK1 and PDK4. However, the activity of PDK4 is also affected by decreased levels of fatty acids and metabolites derived from β-oxidation. Hence, PDK4 appears to be more involved in the regulation of PDH activity in the chronically hypoxic heart. Decreased expression and activity of PDK4 reduce the phosphorylation of PDH, which maintains its active state. PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; PDK, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase; PDP, pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase; Pi, inorganic phosphate; FFA, free fatty acids; NADH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide.