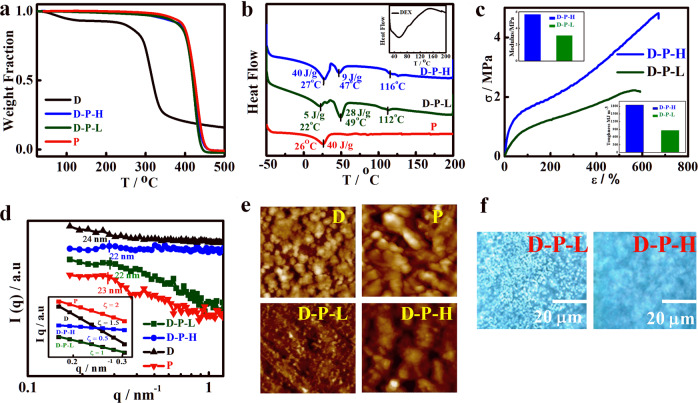
Fig. 2.
Thermal, mechanical and morphological behavior of brush copolymer. a TGA thermograms of pure dextrin, prepolymer (P), and their grafts D-P-L and D-P-H showing their relative thermal stability. b DSC thermograms of P, D-P-L, and D-P-H indicating the melting temperature and heat of fusion values. The inset figure represents the melting pattern of pristine dextrin. c Stress–strain curves of two different brushes (D-P-L and D-P-H) showing their relative strength. Inset bar graphs indicate the modulus and toughness of the brush copolymers. d Small-angle neutron scattering profile of dextrin, prepolymer, and their brushes. Debye–Bueche fittings of the initial data points with correlation length are provided in the inset figure. e AFM images of dextrin, prepolymer, and their brushes in semi-contact mode (10 × 10 μm2). f Optical images of the brush copolymers showing greater agglomerates