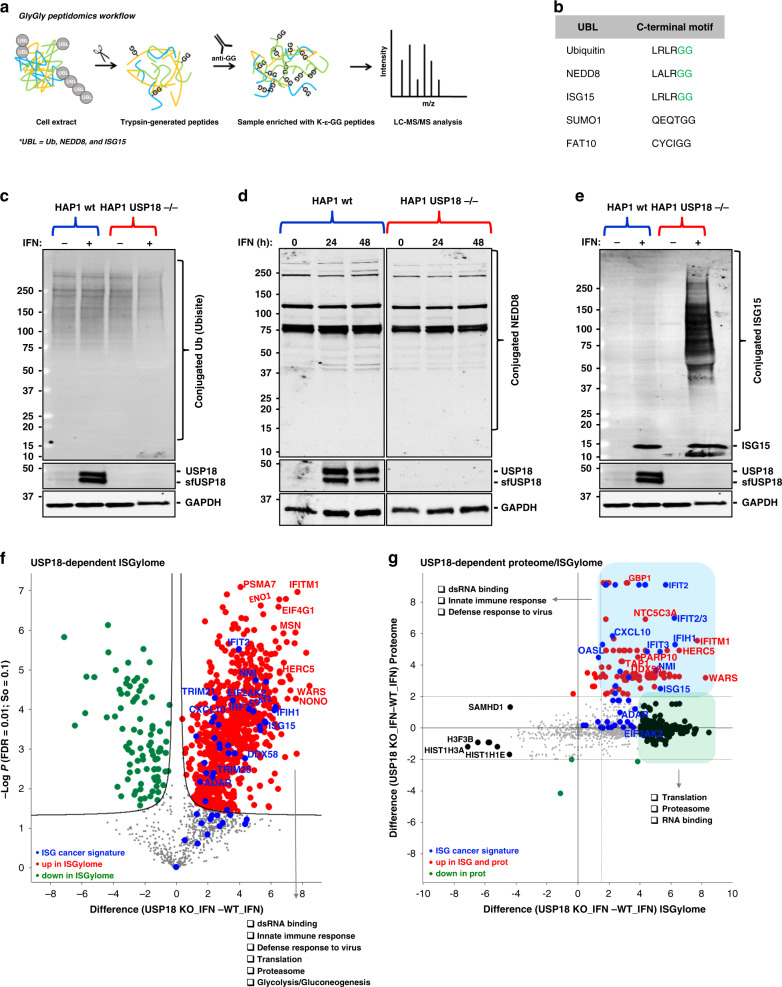
Fig. 2. USP18 is the major cellular de-ISGylase.
a Workflow for analysis of GlyGly-modified peptides. b Comparative table of the C-terminal motifs of the different ubiquitin-like proteins. ISG15, Ubiquitin, and NEDD8 leave a unique GlyGly motif (in green) after trypsin digestion of modified proteins. c Ubiquitin-conjugated and d NEDD8-conjugated proteins do not increase after stimulation with type I interferon (IFN) in USP18 KO cells. e ISG15 modification is accumulated in the same conditions as in (c). f Comparative volcano plot of the GlyGly-modified peptides in HAP1 WT and USP18 KO cells treated with IFN for 48 h showing a strong and significant USP18-dependent upregulation of GlyGly-modified peptides in the KO cells treated with IFN for 48 h. In red are shown the upregulated peptides in the KO cells, in green the upregulated peptides in WT cells, and in blue the modified peptides from an ISG-cancer signature5 (the statistical cut-off values used for all the proteomic analyses performed in this study are FDR: 0.01 and s0: 0.1). Pathway enrichment analysis showed the upregulated peptides in the USP18 KO cells come from proteins involved in the indicated biological processes. g Scatter plot of the cross-comparative analysis of ISGylome and proteome in the same conditions as (f). In red are shown the upregulated ISGylated proteins in the KO cells, in green the upregulated modified proteins in WT cells, and in blue the modified proteins from an ISG-cancer signature.5