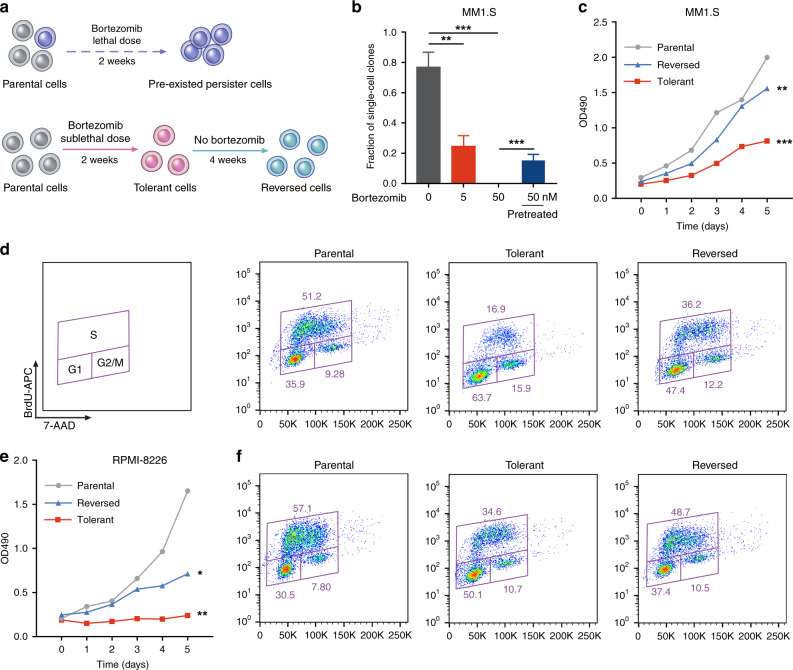
Fig. 2. Reversible resistant MM cells are derived from slow-cycling tolerance.
a Schematic illustrating the formation of pre-existed persister and acquired tolerant cells. b MM1.S single cells were sorted into individual wells and cultured at the indicated concentrations of bortezomib or pretreated with bortezomib for 4 weeks and then treated with 50 nM bortezomib. Red column, unpretreated; blue column, sublethal bortezomib pretreated. Bar plots show the fraction of single cells that form colonies (sorted single cells per condition: n = 288; pooled from 3 independent experiments). c Proliferation of the indicated MM1.S cells for 6 days (three independent biological replicates with three technical replicates each). d Cell cycle profiling of the indicated cells. The fraction of cells viable in G1, S, and G2/M phases of the indicated MM1.S cells is shown. e Proliferation of the indicated RPMI-8226 cells for 6 days (three independent biological replicates with three technical replicates each). f Cell cycle profiling of the indicated cells. The fraction of cells viable in G1, S, and G2/M phases of the indicated RPMI-8226 cells is shown. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; two-tailed t test. Data are represented as mean ± SD.