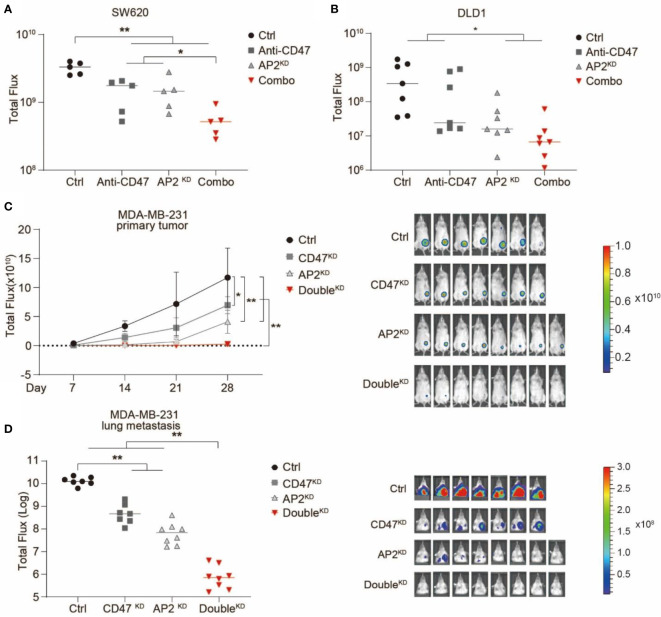
Figure 4.
Suppression of ATP6AP2 expression inhibited tumor growth and metastasis in in vivo mouse models and synergized with CD47 blockade to yield a dramatic anticancer effect. (A, B) Growth of tumors developed by SW620 cells (A) and DLD1 (B) in RAG2−/− γc−/− mice. Mice engrafted with CtrlKD cells or ATP6AP2KD cells were treated with PBS or anti-CD47 antibody. Tumor growth was measured by bioluminescence imaging. (n=5 for SW620 model and n=7 for DLD1 model, at 21 days after tumor engraftment). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (t test). (C, D) Growth (C) and metastasis (D) of tumors developed by MDA-MB-231 cells in RAG2−/− γc−/− mice. Mice orthotopically engrafted with CtrlKD, CD47KD, AP2KD, or double knockdown (DoubleKD) MDA-MB-231 cells. Tumor growth and metastasis were measured by bioluminescence imaging (n=7, 7, 8, 8). In (C) Left, Tumor growth curve, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (t test); Right, animal image from different groups. In (D) Left, luminescence signals of lung metastases at day 35, **P < 0.01 (t test); Right, animal image from different groups.