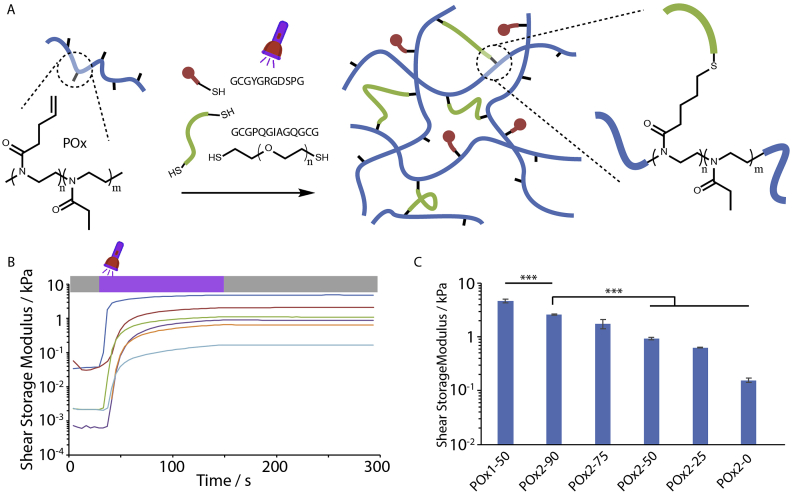
Fig. 1.
Poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) hydrogel assembly and mechanical properties. A. Schematic representation of POx hydrogel assembly and chemical structure. Polymer backbone (blue) combined with crosslinking GIA di-cysteine peptides/PEG dithiol (green) and cell-adhesive RGD peptides (red). B. Impact of the crosslinker composition (PEG/GIA) on gelation of POx hydrogels. Photo-rheology experiments indicating that shear storage moduli reach a plateau after 120 s of photoirradiation. Experimental conditions: POx concentration: 91.1 or 60.7 mg/mL; thiol/alkene ratio of 0.5/1 or 0.9/1, 10 mol% RGD, 3 mol% I2959 photoinitiator and 120 s UV exposure (see Table 1 for details of compositions; mol% correspond to the total moles of alkene, apart from the initiator, which corresponds to the total moles of thiols). Blue, POx1-50; red, POx2-90; green, POx2-75; purple, POx2-50; orange, POx2-25; turquoise, POx2-0. C. Corresponding shear storage moduli extracted from frequency sweeps at a frequency of 1 Hz and a strain of 0.4% (errors shown are standard errors from three independent measurements). ***p < 0.001. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)