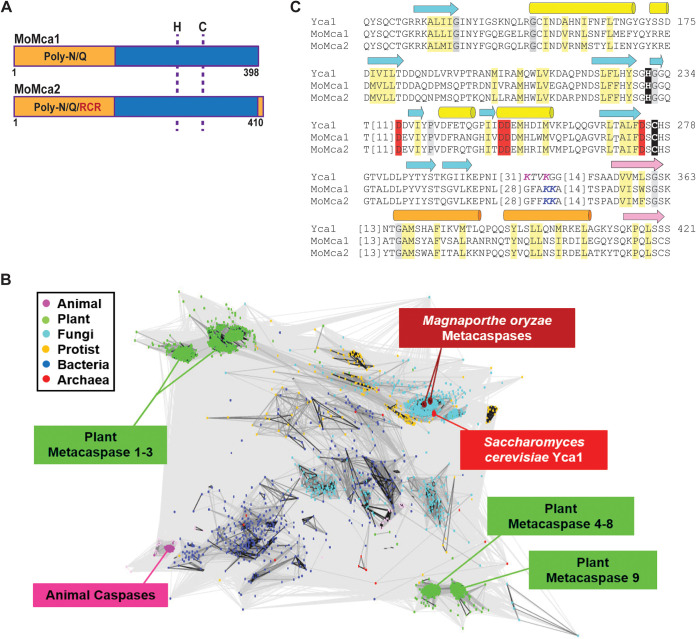
FIG 1.
Bioinformatics identification of two Magnaporthe oryzae metacaspases. (A) Schematic representation of MoMca1 (MGG_04926) and MoMca2 (MGG_13530). The prodomain, rich in asparagine (N) and glutamine (Q) residues, is indicated in orange. The caspase domain is marked in blue. RCR domain, partial sequence motif of chitin synthesis regulation, labeled in red. Dashed lines show the position of the histidine (H) and cysteine (C) catalytic dyad. (B) CLANS clustering analysis is represented graphically as the network of BLAST-derived sequence similarities between 2,712 metacaspase protein sequences. Dots represent sequences, with the shade of connecting lines denoting similarity from gray (low) to black (high). (C) The catalytic sites of MoMca1 and MoMca2 are aligned with Yca1, highlighting conserved active-site residues (black), calcium binding residues (red), Yca1 cleavage site (magenta), predicted MoMca1/MoMca2 cleavage site (Blue), mainly hydrophobic positions (light yellow), and mainly small positions (gray). Beta-strands (arrow) and alpha-helices (cylinder) from the Yca1 structure are indicated above the alignment and colored cyan/yellow before and pink/orange after the cleavage site (italics).