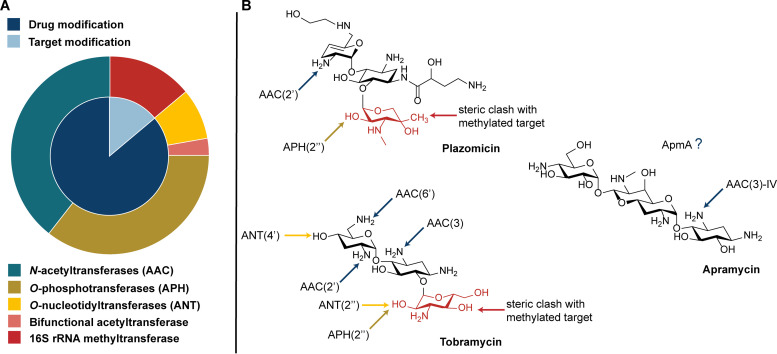
FIG 1.
Apramycin’s advantage to overcome aminoglycoside resistance in the clinic. (A) Aminoglycoside resistance elements explored in this study (Table 1; Fig. S1). Inner circle represents the two main modes of aminoglycoside resistance, drug inactivation and target modification. Outer circle highlights the individual enzymes (Fig. S1), colored based on chemical modification made to the target or antibiotic. (B) Apramycin’s unique monosubstitution of the DOS ring with the octadiose element limits the number of inactivating mechanisms. Lack of substitution at C6 allows avoidance of clinically relevant 16S rRNA methyltransferases.