FIGURE 2.
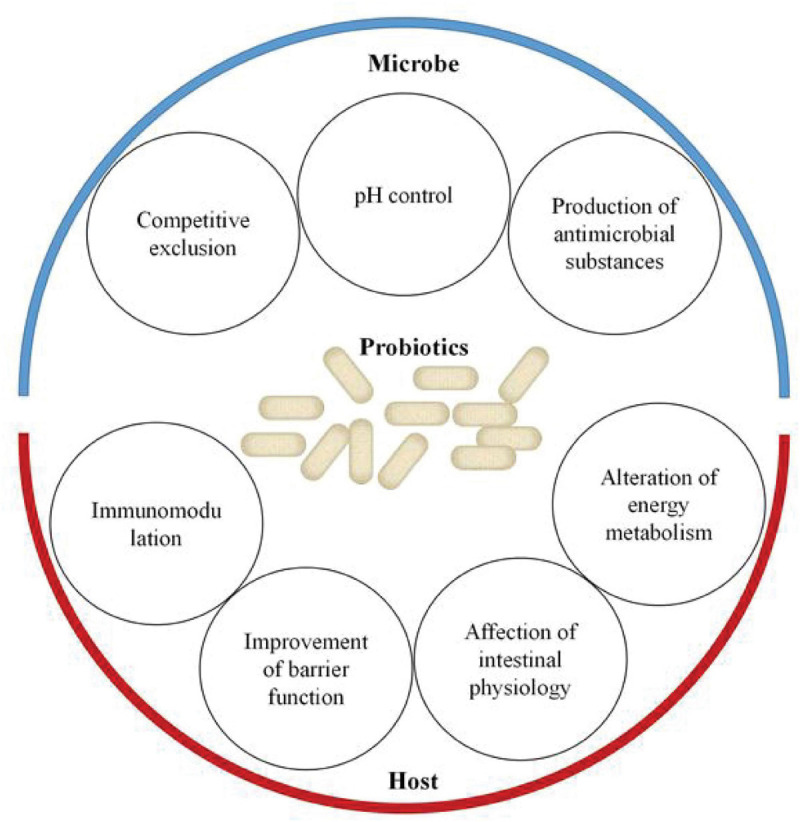
Effects of probiotics on the host–microbe interactions. Probiotics support the stability of the bacterial community and restore the “signature” of gut microbiota through competitive exclusion, pH control, and production of antimicrobial substances. On the other hand, probiotics promote health benefits for the host through improvement of barrier function, immunomodulation, affection of intestinal physiology, and alteration of energy metabolism.
