Fig. 1.
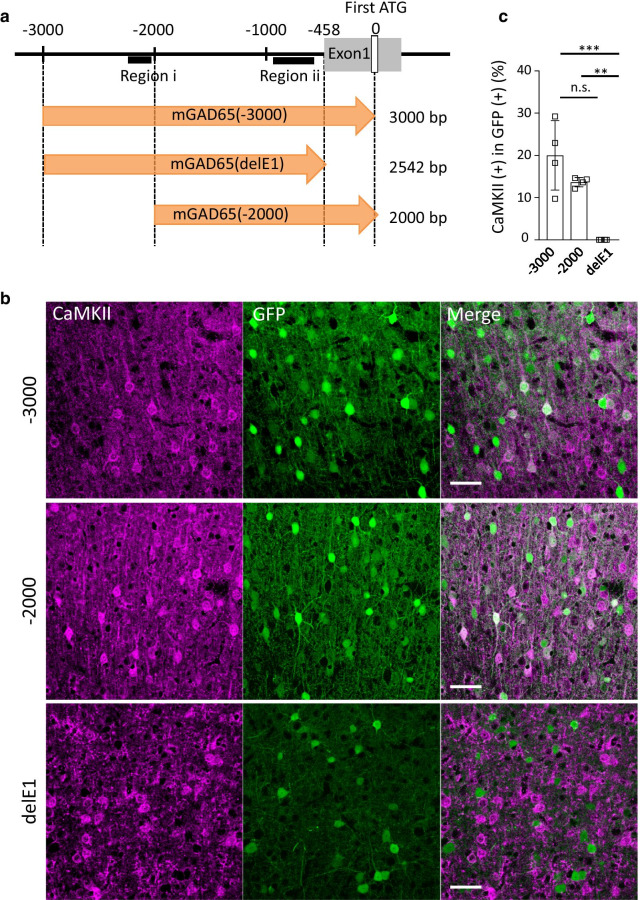
Inhibitory neuron-specific mGAD65 promoter candidates and their screening using immunohistochemistry. a Schematic displaying mouse Gad2 (mGAD65) promoter regions examined as candidates for the inhibitory neuron-specific promoter. Mouse genomic regions (3000, 2542, and 2000 bp) upstream of the first ATG codon (position 0) in exon 1 of the Gad2 gene were cloned from C57BL/6-mice cDNA library. mGAD65 (delE1) shares most portions with mGAD65 (-3000), but it lacks the exon 1 sequence. Black bars (Regions i and ii) depict relative positions of the TAAT/ATTA motif, a core sequence for homeodomain protein binding. b Immunohistochemistry of the motor cortices obtained from mice that received intravenous infusions of AAV-PHP.eB expressing GFP by one of the promoters described in a. The brain sections were double immunolabeled for GFP and CaMKII, a marker of the excitatory neurons in the cerebral cortex. Scale bars; 50 μm. c Quantitative analysis of each promoter candidate in terms of the specificity for inhibitory neurons. Ratios of CaMKII-expressing (double-positive) excitatory neurons to total GFP ( +) cells were measured. For respective promoter candidates, we examined 4 visual fields in 2 sections from one animal. The value obtained from each visual field was plotted. We found 29 double-positive cells in 147 GFP ( +) cells (20.0 ± 3.6%) for the mGAD65 (− 3000), and 18 double-positive cells in 131 GFP ( +) cells (13.7 ± 0.5%) for the mGAD65 (− 2000); no double-positive cells were found in 75 GFP ( +) cells (0.0 ± 0.0%) for the mGAD65 (delE1). ***p = 0.0007, **p = 0.0089 and p = 0.28 by ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test