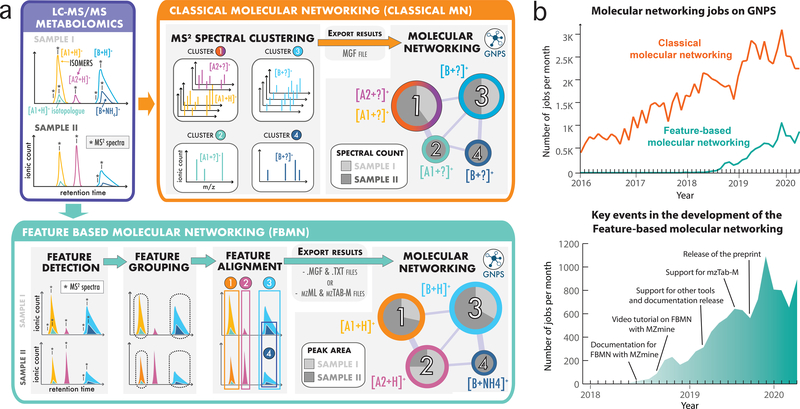
Fig. 1: Methods for the generation of molecular networks from non-targeted mass spectrometry data with the GNPS web platform.
a) Two methods exist for the generation of molecular networks on the GNPS web platform: classical MN and feature-based molecular networking (FBMN). For both methods, the mass spectrometry data files have first to be converted to the mzML format using tools such as Proteowizard MSConvert21. The classical MN method runs entirely on the GNPS platform. In that method, MS2 spectra are clustered with MS-Cluster and the consensus MS2 spectra obtained are used for molecular network generation. In the case of FBMN, the user first applies a feature detection and alignment tool to first process the LC-MS2 data (such as MZmine, MS-DIAL, XCMS, OpenMS, Progenesis QI, or MetaboScape) instead of using MS-Cluster (classical MN) on GNPS. Results are then exported (feature quantification table (.TXT format) along with a MS2 spectral summary (.MGF format) or an mzTab-M file) and uploaded to the GNPS web platform for molecular networking analysis with the FBMN workflow. b) Graphs showing the number of molecular networking jobs performed on GNPS. The upper graph shows the number of classical MN and FBMN jobs since 2016. The lower graph shows the number of FBMN jobs since its introduction in 2017 and key events accelerating its use.