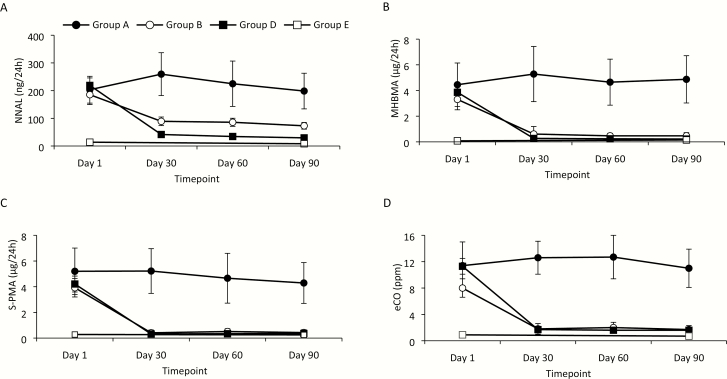
Figure 1.
Changes in biomarkers of exposure over time in the CEVal-compliant population. Plots show absolute levels of 24-hour urinary excretion of (A) 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanol (NNAL), (B) monohydroxybutenyl-mercapturic acid (MHBMA), (C) S-phenylmercapturic acid (S-PMA), and (D) exhaled breath carbon monoxide (eCO) at baseline (day 1, all groups) and at days 30, 60, and 90 (smokers at baseline [Groups A, B, and D]) or at day 90 (never-smokers [Group E]). Data are presented as means ± CI in subjects in the CEVal-compliant population who continued to smoke combustible cigarettes (Group A; n = 32), switched to using glo (Group B; n = 60), abstained from cigarette smoking (Group D; n = 107), or were never-smokers (Group E; n = 35). The legend in panel A is applicable to all other panels.