Figure 1.
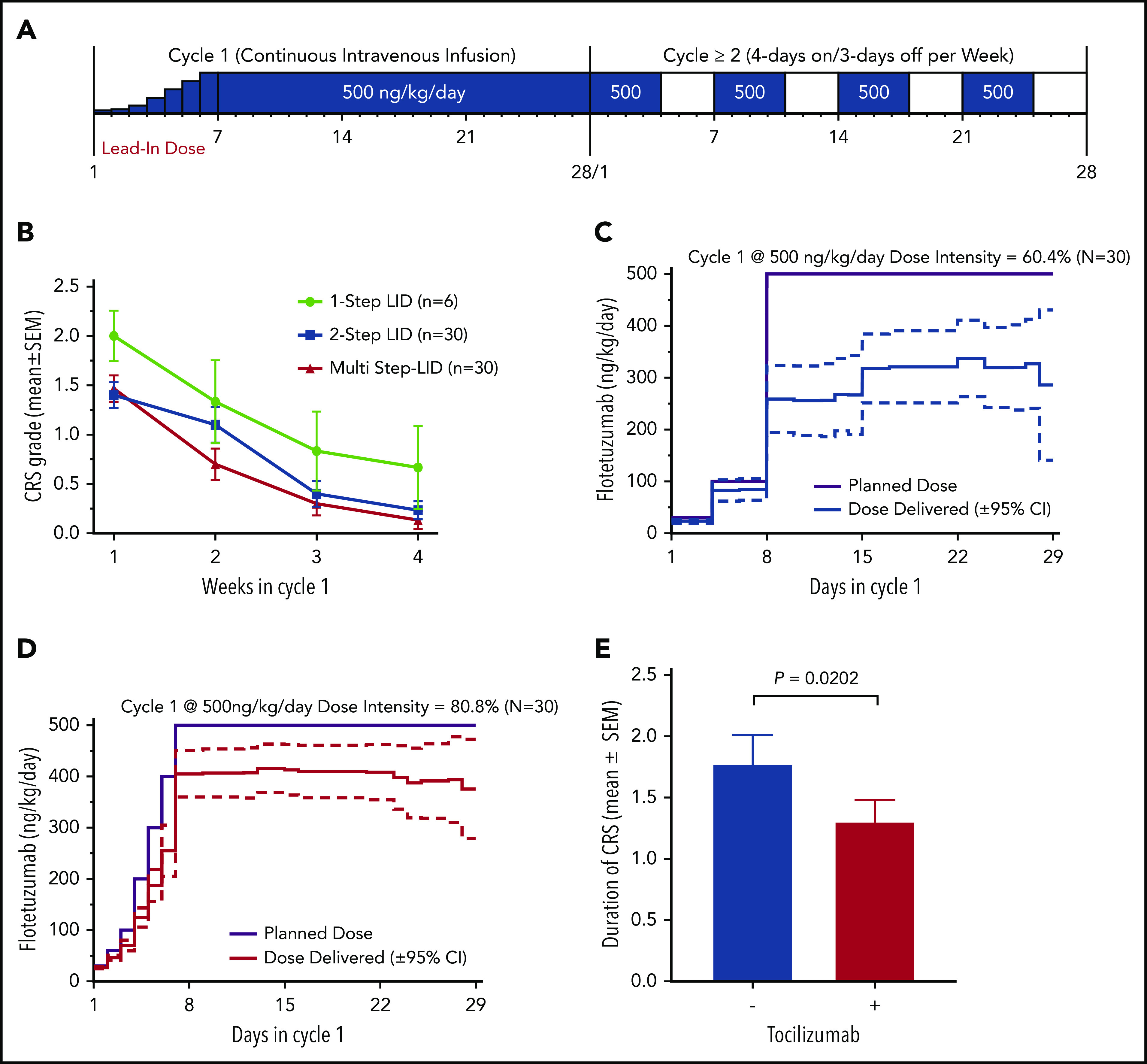
LID and use of tocilizumab decrease CRS incidence, severity and duration, and lead to increase in total dose intensity. (A) Summary of dose and dosing schedule for flotetuzumab: MS-LID of 30, 60, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500 ng/kg per day for 24 hours each for days 1 through 7 given via CIV infusion, followed by 500 ng/kg per day CIV from days 8 to 28 during cycle 1, with subsequent additional 28-day cycles dosed at 500 ng/kg per day doses intermittently 4 days on/3 days off per week in 28-day cycles without LID lead-in. (B-D) LID mitigates CRS and consequently leads to improvement in dose intensity. (B) CRS grade (mean plus or minus standard error of the mean [SEM]) during each week of cycle 1. (C-D) Dose intensity (percentage, mean plus or minus 95% CI) was calculated as the amount of drug received during the time on study (actual drug delivered) relative to the intended dose during weeks 2 to 4 following respective LID during week 1 of 2-step (left) multistep (right) LID. (E) Tocilizumab effect on duration of IRR/CRS, irrespective of grade. Only patients for whom the drug was not modified as a method of controlling IRR/CRS are included. Mean duration of CRS without tocilizumab 1.8 days (n = 42) and with tocilizumab 1.2 days (n = 13); P = .0202, Student t test.
